* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection - Boyd County Schools
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
On the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
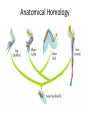
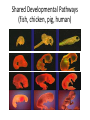
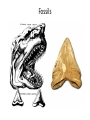
Natural Selection A Brief Overview “Descent with Modification” • Species change over time = hot idea in 1700’s • G. Cuvier noted fossils in rock strata – “Catastrophism” explains abrupt changes in fossils • C. Lyell, geologist, was for “uniformitarianism” – Geological forces of past still working today • J.B. Lamark supported spontaneous generation & inheritance of acquired traits – Neither of these explanations is accepted today Lexington, KY: Ordovician Period Fossils 450 million years ago “Descent with Modification” “Natural Selection” • Evolution proposed by others already – Anaximander (611-546 B.C.) 1st Westerner – Erasmus Darwin (Charles’ grandfather) • Charles Darwin & Russell Wallace present idea of evolution to scientific community in France • Charles Darwin (1859) published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection. – Descent with Modification = process of evolution – All current life descended from 1 (or few) life forms – Species must be able to change over time Darwin’s Grounds for Evolution • Observations during sea trip around world – Galapagos Islands’ distinct populations • Finches, tortoises, mockingbirds, etc… – Plant & animal comparisons among continents • Prickly pear, octopus, birds, insects, lizards, mice, coral • Writings from Lyell on fossils & rock strata • Notes from grandfather Erasmus Darwin • T. Malthus’ writings on population pressures Basis For Natural Selection 1) Overproduction More offspring are produced than can survive. 2) Genetic Variation Individuals have range of traits. 3) Struggle to Survive Competition and Adaptation favor “best fit”. 4) Differential Reproduction “Adaptation”- best survive & out-reproduce others “Acclimatization” – personal adjustments Evidence for Evolution I • Biological Linnaean Classification – Implied evolutionary relationships • Anatomical Homology – Mammalian forelimbs have same bones • Vestigial Structures – Traits remain longer than their function does • Humans’ appendix • Whales’ pelvic bone • Penguins’, ostriches’, emus’, et al. wings Anatomical Homology Vestigial Structures Evidence for Evolution II • Shared developmental pathways – Similarity among embryos of same families • DNA homology – Closer related organisms have greater % homology • Biogeography – Species geographically share common ancestor • Fossils – Direct evidence of changing organisms over time Shared Developmental Pathways (fish, chicken, pig, human) DNA Homology DNA Homology II Biogeography Fossils Coevolution Artificial Selection