* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction grating wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Refractive index wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Smart glass wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Wave interference wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
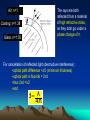
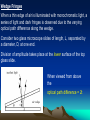
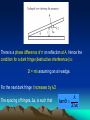
Non-reflective coating Good quality lenses in a camera reflect very little light and appear dark or slightly purple. A thin coating of a fluoride salt such as magnesium fluoride on the surface of the lens allows the majority of the light falling on the lens to pass through. The refractive index, n, of the coating is chosen such that 1 < n < nglass Air: n=1 Coating: n=1.38 Glass: n=1.50 Air: n=1 The rays are both reflected from a material of high refractive index, so they both go under a phase change of π. Coating: n=1.38 Glass: n=1.50 For cancellation of reflected light (destructive interference) : •optical path difference =λ/2 (minimum thickness) •optical path in fluoride = 2nd •thus 2nd =λ/2 •and d λ 4n Wedge Fringes When a thin edge of air is illuminated with monochromatic light, a series of light and dark fringes is observed due to the varying optical path difference along the wedge. Consider two glass microscope slides of length, L, separated by a diameter, D, at one end. Division of amplitude takes place at the lower surface of the top glass slide. When viewed from above the optical path difference = 2t There is a phase difference of π on reflection at A. Hence the condition for a dark fringe (destructive interference) is: 2t = mλ assuming an air wedge. For the next dark fringe t increases by λ/2 The spacing of fringes, Δx, is such that λ tanθ 2 x Giving λ Δx 2tanθ For a wedge of length L and spacing D. D tanθ L The fringe spacing is given by λL Δx 2D where λ is the wavelength of light in air.