* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Continental Drift - sciencewithskinner
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
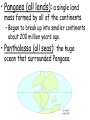
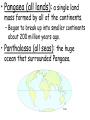
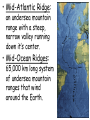
• Chapter 8, Section 1 Objectives: 1. Explain Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift. 2. List evidence for Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift. 3. Describe seafloor spreading. • Continental Drift (1912): the hypothesis proposed by Alfred Wegener, which stated that the continents had moved. • Pangaea (all lands): a single land mass formed by all of the continents. – Began to break up into smaller continents about 200 million years ago. • Panthalassa (all seas): the huge ocean that surrounded Pangaea. • Pangaea (all lands): a single land mass formed by all of the continents. – Began to break up into smaller continents about 200 million years ago. • Panthalassa (all seas): the huge ocean that surrounded Pangaea. • Pangaea (all lands): a single land mass formed by all of the continents. – Began to break up into smaller continents about 200 million years ago. • Panthalassa (all seas): the huge ocean that surrounded Pangaea. • Evidence of Continental Drift: 1. Fossil – links between Africa and South America • Evidence of Continental Drift: 2. Geological - Age and type of rocks match - Mountain ranges fit together • Evidence of Continental Drift: 3. Climatic -Matching layers of debris from glaciers in areas that are warmer today - Fossil evidence (coal deposits) indicate a matching tropical or subtropical swamps in the northern hemisphere 4. Seafloor spreading 5. Paleomagnetism • Despite evidence, most scientists disbelieved the hypothesis! • Seafloor Spreading (1947): Magma or molten rock welling up through rift in center of mid-ocean ridge, as ocean floor moved away from both sides of ridges. • Mid-Atlantic Ridge: an undersea mountain range with a steep, narrow valley running down it’s center. • Mid-Ocean Ridges: 65,000 km long system of undersea mountain ranges that wind around the Earth. • Evidence of seafloor spreading: – Age of rocks • Oldest oceanic rocks no more than 150 million years old • Oldest continental rocks are about 4 billion years old • Paleomagnetism of the ocean floor (1960’s) – Magma cools and iron-bearing minerals become magnetized – Orientation becomes permanent pointing north Normal magnetic polarity Points north • Paleomagnetism of the ocean floor (1960’s) – Scientists have found bands pointing south – Earth’s magnetic field must reverse itself – Verified by dating of rocks Reverse magnetic polarity Points south