* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
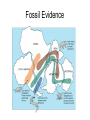
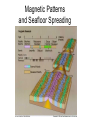
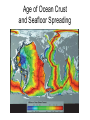
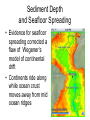
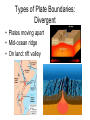
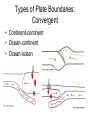
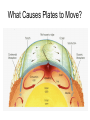
Chapter 17 Plate Tectonics Drifting Continents: Early Observations • Cartographers were the first people to notice matching continents Antonio Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Alfred Wegener • German meteorologist/climatologist • 1912: proposed the idea of continental drift – Continents started as “Pangea” 200 million years ago – Slowly moving apart to present positions Evidence for Continental Drift • Matching coastlines • Matching rock formations/mineral deposits separated by oceans • Climate evidence: fossil ferns Glossopteris) found in Antarctica, South America, and India • Matching fossils on widely separated continents (Cynognathus, Lystrasaurus, Mesosaurus) Fossil Evidence Flaws of Continental Drift • Did not explain the immense forces required to move continents long distances • No evidence of continents “plowing through” the ocean crust • Continental Drift was rejected until the early 1960s, when these flaws were resolved Seafloor Spreading • Technology advances in the 1940s and 1950s led to more detailed ocean floor mapping • Magnetometer: detects changes in magnetic fields • Sonar: found mid-ocean ridges and deep sea trenches • Interesting patterns in age of rock samples Magnetic Patterns and Seafloor Spreading Age of Ocean Crust and Seafloor Spreading Sediment Depth and Seafloor Spreading • Evidence for seafloor spreading corrected a flaw of Wegener’s model of continental drift • Continents ride along while ocean crust moves away from mid ocean ridges Types of Plate Boundaries: Divergent • Plates moving apart • Mid-ocean ridge • On land: rift valley Types of Plate Boundaries: Convergent • Continent-continent • Ocean-continent • Ocean-ocean Types of Plate Boundaries: Transform • Plates slide horizontally past each other What Causes Plates to Move?