* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
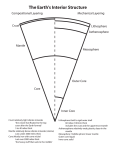
Download Layer Depth (km) Rigidity
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Class #3 -- Geology 117 EARTH 2: Structure, origin, age •Internal zones •Age of Earth •Origin of the oceans and atmosphere •Important events in Earth history Layering of the Earth Based on Rigidity Layering in the earth (based on rigidity) Layer Depth (km) Rigidity Lithosphere 150 beneath continents 70 beneath oceans (includes some mantle!) Rigid (elastic) Asthenosphere Bottom of Lithosphere to about 250 km Ductile (plastic) Rest of Mantle Bottom of Asthenosphere to the core Ductile, but stronger The Mantle is NOT LIQUID • Maybe small amounts of liquid in tiny pores in the asthenosphere, BUT ~99%+ solid • BUT…Mantle is plastic over long distances and time, very slowly “creeping” to change shape Solids can flow very slowly http://www.extremeicesurvey.org/index.php/new _gallery/timelapse_1/ Origin of Atmosphere •Early H2 and He (light gases)-- “blown away” •Release of gases from interior N2, CO2, CH4, NH3, H2S, HCl, H2O vapor. •Evolution of atmosphere: (a) loss of reactive gases; (b) development of life – much later... CO2 removed and O2 accumulated. Origin of Oceans • Formed very early in earth history • Cooling; condensation of water vapor • Acid rain: from acid gases in atmosphere • Reaction with surface rocks to form dissolved products and sediments • Little change in oceans through time: -- Salinity and area remained ~ constant -- depth and volume increased a little Earth History Geologic Time Scale •based on record in rocks of "events" •mountain building •fossil evolution •radiometric dating gave "absolute" ages (in years). Geologic Time Scale: Fig. 1.24 Earth History Important events: •Origin of Earth: 4,600 m.y. •Appearance of "oceans": ~4,400 m.y. •Oldest preserved rock on continents: 4,200 m.y. •First bacteria: ≥3,800 m.y. •Photosynthesizing algae appear: ~3,000 m.y. •O2 in the atm.: ~2,000 m.y. •Multicellular organisms: ~600 m.y. •First "hominids": ~4 m.y. Represents amount of uranium Represents amount of lead Oxygen in the atmopshere •O2 NOT present before life evolved!!! •Photosynthesis can generate O2 •Need carbon- use CO2 from atmos. •Remove the O’s, use the C’s •Build living tissues with C-rich organic matter •Waste Product: O2 •Builds up only if organic matter is buried •Initially toxic to life •Eventual adaptation- led to higher organisms? Fig. 1.20 Fig. 1.19