* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Soil Composition
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
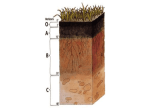
Soil Composition In this presentation you will: explore the process of soil formation explore the composition of soil explore how human activity can damage the soil Next > Soil Composition The loose, top layer of the Earth’s surface is made of soil. This is called the pedosphere. Atmosphere The pedosphere interacts with the four major systems of the Earth: Geosphere Geosphere – the solid part of the Earth Hydrosphere Atmosphere – the layer of gases surrounding the Earth Biosphere Hydrosphere – all water on Earth Biosphere – all living organisms Next > Question 1 What is the name given to the top layer of the Earth's surface that is composed of soil? A) Pedosphere B) Atmosphere C) Geosphere D) Hydrosphere Next > Question 1 What is the name given to the top layer of the Earth's surface that is composed of soil? A) Pedosphere B) Atmosphere C) Geosphere D) Hydrosphere Next > Soil Composition Soil contains four types of materials: Minerals – contained in rock, sand, clay, and silt Organic material (substances containing carbon atoms derived from living organisms) Soil surface Pores Pores Water – soil contains holes (pores) that fill with water Air – pores in soil may also fill with air Pores Next > Soil Formation Soil formation is a slow process. It can take hundreds or even thousands of years to make just one handful. Soil is mostly formed from rocks which have been weathered, or broken down to form sediment. The rock from which soil is formed is referred to as parent material. The weathering of parent material can take place in one of two main ways: Physical weathering Chemical weathering Next > Physical Weathering Physical weathering is the process by which rocks are broken down into soil. It is usually the effect of water, wind, ice, pressure, or heat. For example, a drop in temperature can cause water that has seeped into rock cracks to freeze. As the water freezes, it expands, pushing the rocks apart. Next > Chemical Weathering Chemical weathering is the process by which the chemical makeup of rock is changed, causing it to deteriorate. For example, water can contain dissolved chemicals that cause rock to break down. Chemical weathering occurs naturally, but can also be caused or accelerated by pollution. Harmful chemicals that are released into the atmosphere as a result of human action dissolve in rain water to create acid rain. When acid rain falls, it causes rocks to crumble and disintegrate. Next > Question 2 "Parent rocks can be physically weathered by water." Is this statement true or false? Next > Question 2 "Parent rocks can be physically weathered by water." Is this statement true or false? True Next > Erosion and Deposition Soil is often formed from parent material that is not found in the area where the soil is located. This is due to the processes of erosion and deposition. Erosion occurs when solid particles, known as sediment, are moved by wind, water, ice, or gravity. Sediment may contain organic material, rock or soil. Sediment transported by erosion is eventually deposited in a new location. The deposited sediment then becomes part of the soil in the new location. Next > Minerals Rocks contain minerals. Minerals are naturally occurring solid substances. Minerals are inorganic, which means they do not contain carbon atoms. Rocks may be composed of a single mineral or many different minerals. For example, limestone rock is made from one mineral (calcite) but sand is made up of several different minerals, such as silica and mica. Soil contains the minerals of its parent rocks. Next > Organic Material Organic material found in the soil consists of decomposed dead organisms, such as fallen leaves and dead animals, as well as living organisms. Many organisms live in soil. Underneath every footprint that you make in soil are thousands of organisms. Most organisms, such as earthworms, fungi, and insect larvae, are beneficial to the soil. However, some can be harmful and bring damage to crops, and disease to animals and people. Next > Beneficial Organic Material Decomposing organic material contained in soil is known as detritus. One of the most common forms of detritus is leaf litter. Detritus is broken down by decomposers, which are organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that live in the soil. Dead organisms contain nutrients. When decomposers break down detritus, these nutrients are released into the soil. Other organisms, such as earthworms, move detritus around, helping to spread nutrients throughout the soil. Next > Beneficial Organic Material As detritus decomposes, it becomes a brown substance called humus. Humus contains important nutrients and retains moisture. Plants grow at their best in areas of soil that are rich in humus. If the soil is lacking in nutrients, fertilizers (substances containing extra nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus) can be mixed in with the soil to encourage plant growth. Fertilizers are commonly used in farming and gardening. Nutrients added Nitrogen Phosphorus Next > Question 3 Which of the following statements is true? A) Detritus is the name given to inorganic material in the soil B) Decomposers break down detritus C) Humus is another name for detritus D) All of the above Next > Question 3 Which of the following statements is true? A) Detritus is the name given to inorganic material in the soil B) Decomposers break down detritus C) Humus is another name for detritus D) All of the above Next > Harmful Organic Material Most soil organisms are beneficial to other organisms that use soil, but there are a few which are harmful. The bacteria Clostridium tetani is found in most soils. It enters organisms through broken skin wounds, and causes the disease known as tetanus, which can paralyze muscles. People who regularly work outdoors must ensure that they are vaccinated against soil-borne diseases such as tetanus. Next > Water and Air Rainwater seeps into soil pores. Soil surface Pores Pores Pores of various sizes retain the water, making it easy for plant roots and soil organisms to access the water they need. Water is used in many metabolic reactions in living organisms. Pores Water Pores also hold air so that soil organisms that require oxygen to live can breathe and survive under the ground. Oxygen Next > Question 4 Which of the following statements is true? A) Water and air are held in pores in the soil B) Soil pores are various sizes C) Water is needed for many metabolic reactions D) All of the above Next > Question 4 Which of the following statements is true? A) Water and air are held in pores in the soil B) Soil pores are various sizes C) Water is needed for many metabolic reactions D) All of the above Next > Life and Soil Soil supports most of the plant life on Earth. This is why it is important that we look after our soil. In areas all around the world, soils are being damaged because of human activity. Soils are being stripped of their nutrients, and with it, their ability to support life. The greater the soil quality, the more organisms it can support. Next > Damaging Activities There are several ways in which soil damage can occur: Soil mining – Farming of the same crop in the same area for a long time can drain the soil of its available nutrients, as can over-grazing by animals. Chemicals – Insecticides and herbicides (used to kill harmful insects and weeds) sprayed onto crops change the acidity of the soil. This can cause changes in all areas of an environment. Next > Damaging Activities Landfill sites – Over half of our trash is buried underground in landfill sites. Toxic chemicals from the trash can leak into the soil, killing organisms that live in or rely on the soil. Construction – Soil and plant life is wiped away for the creation of houses and buildings. Tarmac and concrete do not let air and water through, so the soil below it cannot support life. Next > Question 5 Which of the following problems is associated with soil mining or overgrazing by animals? A) Changes in soil acidity B) Leaking of toxic chemicals C) Lack of air and water in the soil D) Lack of nutrients in the soil Next > Question 5 Which of the following problems is associated with soil mining or overgrazing by animals? A) Changes in soil acidity B) Leaking of toxic chemicals C) Lack of air and water in the soil D) Lack of nutrients in the soil Next > Damaging Activities Hedges and trees are often removed to make way for agricultural land. Plants protect soil from erosion. When plants are removed, soil is blown away by wind and carried away by rain. The Dust Bowl, which formed in the central United States and Canada in the 1930s, was caused by soil erosion resulting from over-production of crops and the over-plowing of soils. Similar problems are now occurring in parts of Africa, resulting in fertile land becoming a desert, or desertification. Next > Soil Conservation In order to stop more soil from being damaged, humans must limit these damaging activities. We can renew already damaged soil by methods known as soil conservation. However, these methods can take a long time to repair the damage. Reforestation is a method of repairing damaged areas of land by planting new plants and trees to replace those that have been removed. This helps to protect the soil from further erosion and attracts many forms of life back into the area. Next > Summary In this presentation you have seen: soil composition and the formation of soil human activities that can damage the soil End