* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Boring Billion wikipedia , lookup
Phanerozoic wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
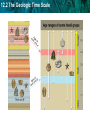
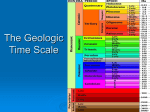
12.2 The Geologic Time Scale KEY CONCEPT The geologic time scale divides Earth’s history based on major past events. Tollund Man: • Died about 2200 years ago in what is now Denmark. • Details such as his skin and hair were preserved by the bog in which he was found. A bog is a type of wetland that accumulates peat, the deposits of dead plant material. 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale Index fossils are another tool to determine the age of rock layers. • Index fossils can provide the relative age of a rock layer. • Defined as: – Fossils of organisms that existed only during specific spans of time over large geographic areas. • Characteristics: – Common – Easy to identify – Found widely around the world – Only existed for a relatively brief time 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale Index fossils are another tool to determine the age of rock layers. • Examples: – Index fossils include fusulinids and trilobites. • Non-example: – Any fossil that is rare or only found in a certain region. 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale The geologic time scale organizes Earth’s history. • The history of Earth is represented in the geologic time scale. 100 250 550 1000 • Geologic Time Scale: – Representation of the history of the Earth that is organized by major changes or events. • Organized into Eons, Eras, Periods and Epochs. 2000 PRECAMBRIAN TIME This time span makes up the vast majority of Earth’s history. It includes the oldest known rocks and fossils, the origin of eukaryotes, and the oldest animal fossils. Cyanobacteria 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale The geologic time scale organizes Earth’s history. • Eons represent the greatest expanses of time. There are 4 Eons: Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic. 100 250 550 1000 • The Hadean, Archean, and Proterozoic are collectively known as Precambrian Time, from 4.56 billion years ago to 540 million years ago. • Eons are divided into Eras. 2000 PRECAMBRIAN TIME This time span makes up the vast majority of Earth’s history. It includes the oldest known rocks and fossils, the origin of eukaryotes, and the oldest animal fossils. Cyanobacteria 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale The geologic time scale organizes Earth’s history. • Eras: last from tens to hundreds of millions of years and consist of 2 or more Periods. • Periods: last for tens of millions of years and are the most commonly used units of time. Associated with rock systems. • Epochs: last for several millions of years and are the smallest units of time. 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale • Eras last tens to hundreds of millions of years. – consist of two or more periods – three eras: Cenozoic, Mesozoic, Paleozoic 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale Eras last for tens to hundreds of millions of years. 1) Cenozoic Era: Evolution of primates, diversification of mammals, flowering plants. Continues today. 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale Eras last for tens to hundreds of millions of years. 2) Mesozoic Era: Evolution and extinction of dinosaurs, evolution of ferns and cycads and mammals. 12.2 The Geologic Time Scale Eras last for tens to hundreds of millions of years. 3) Paleozoic Era: All existing animal phyla developed, earliest land plants evolved. Liverworts Mosses