* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Soil
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
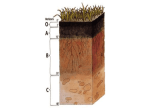
Soil ES SOL 8a DEFINE SOIL • Your Definition • SOL Definition Soil is formed from the weathering of rocks and organic activity and is composed of loose rock fragments and clay derived from weathered rock mixed with organic material. Soil Formation Soil Profile LEACHING Soil and Climate • Tropical Climates – humid and a lot of rain • Soils are very good for growing plants • Lot of humus (20%-30%) • However, lots of rain leaches the material downward and create a very thin soil. • Any removal of vegetation will cause topsoil to erode away and be lost. Soil and Climate • Desert Climates – very dry • Low rate of chemical weathering. • Water moving through the ground will evaporate as it reaches the surface leaving “salts” behind. • Too much salt is toxic to plants. • Salt Flats Soil and Climates • Temperate Climates – “us” – both chemical and mechanical weathering occur. • Not enough rain to leach out nutrients so you have thick fertile soils. • Breadbasket – able to grow wide variety of plants. Soil and Climates • Arctic Climate – much like desert climates, arctic areas can have very little precipitation. “Cold Deserts” • Less chemical weathering and slow soil development. Very few plants can survive in this environment. Soil Conservation • Soil Conservation – the various methods used to take care of the soil. • Importance of soil • Plant Health – better soil = better plants • Housing – burrowing creatures live there. • Storage – soil holds water Soil Texture Triangle • Sand > 0.05 mm • Silt > 0.002 mm • Clay < 0.002 mm • Grain Size Analysis • Sieve Analysis 40% Silt – 40% Sand – 20% Clay = LOAM