* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
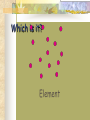
Atoms, Matter & Molecules Science for 4th & 5th Grade! Observations Direct evidence obtained through use of the senses. Inference A hypothesis, drawn from observations, that attempts to explain or to make sense of the observations ATOM The smallest particle into which an element may be divided and still be the same substance. ATOM The smallest part you can break Hydrogen (an element) into and still have Hydrogen. Matter Anything that has mass and takes up space. Energy is NOT matter Matter is divided into 4 components: Elements Compounds Mixtures Solutions ELEMENT All elements are on the Periodic Table All matter is made of an element or a combination of elements Hydrogen, Oxygen, Gold A substance that consists of only one kind of atom and that cannot be chemically separated into other substances. Elements: E l e m e n t s c a n n o t b e changed into simpler substances by any chemical process. E l e m e n t s a r e m a d e u p of atoms. Elements: simplest kind of matter Cannot be broken down into simpler All one kind of atom. There are 109 of these known to man Types of matter Compounds - Pure substances ade up of more n one element. m tha Compounds: substances that can be broken down by chemical methods When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. Made of molecules- two or more atoms Compounds: They are pure substances put together by chemically combining elements Not all combinations of elements are compounds though– some can be mixtures! So remember… ELEMENTS contain only one kind of atom There are 109 different kinds of elements 1-109 = atomic # of the elements. Solutions: Solutions - A special mi xture formed when one su bstance dissolves in another . Solutions: Solvent - the most abundant substance in the solution. Solute - the least abundant substance in the solution. All solutions are not liquids: Air is a of Steel is of solution gases. a solution metals. Solutions Homogeneous mixture Mixed molecule by molecule Can occur between any state of matter. Solid in liquid- Kool-aid Liquid in liquid- antifreeze Gas in gas- air Solid in solid - brass Liquid in gas- water vapor Solutions Like all mixtures, they keep the properties of the components. Can be separated by physical means Do not scatter light! Not easily separated but can be separated. Two techniques for separating solutions: #1. Evaporation: changing from a liquid to vapor state– leaves behind the other component. #2. Distillation: Process used to drive vapor from liquid by heating Great for separating two or more liquids which have different boiling points. MIXTURE Matter that can be physically separated into component parts It is two or more kinds of matter that have separate identities because of their different properties. When different parts of a mixture can no longer be separated into simpler substances, we call each component a PURE SUBSTANCE There are two types of mixtures: Heterogeneousmixture is not the same from place to place. Chocolate chip cookie, gravel, soil. Homogeneoussame composition throughout. Kool-aid, air. •Every part keeps its properties. Mixtures: Matter that consists of two or more substances mixed together: but not chemically combined or bonded. Examples: concrete, Sea Water, a bag full of different colored marbles.. There are 2 types of Mixtures Heterogeneous Mixture: a mixture that does not appear the same throughout. (the individual substances are visible). Ex. Soil, Raisin Brand, Chicken Noodle Soup. Homogeneous Mixture: a mixture that appears uniform throughout. (well mixed). Ex. Stainless Steel (Cr, Fe), Types of matter Properties of Mixtures: E ach substance retains its own properties. S u b s t a n c e s c a n b e sent in any amount. S u b s t a n c e s c a n b e separated by simple p h y s i c a l m e a n s. pre Which is it? Element Which is it? COMPOUND Water is a compound formed from two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom chemically combined. H20 Which is it? MIXTURE Decide if the substance is an E l e m e n t , c o mp o u n d , m i x t u r e , o r s o l u t i o n? 1. Water 1. Compound 2. Salt 2. Compound 3. Oxygen 3. Element 4. Dirt 4. Mixture 5. Air 5. Solution Click Mouse button to see answers! Decide if the substance is an E l e m e n t , c o mp o u n d , m i x t u r e , o r s o l u t i o n? 6. Copper 6. Element 7. Coke 7. Solution/Mixture 8. Steel 8. Solution 9. Rain 9. Mixture 10. Ice-cream 10. Mixture Click Mouse button to see answers! What about MOLECULES? These are MULTI-ATOM particles They are the smallest particle of a substance that still retains the properties of that substance and is composed of 2 or more atoms. MOLECULE Particle of matter that is made up of two or more atoms. MOLECULE The smallest part you can break water (a compound) into and still have water. Particle Charge Location Mass Proton + nucleus heavy Neutron 0 nucleus heavy Electron - energy levels very light Atomic Number The number of protons in the nucleus 17 Cl Chlorine 35.453 Atomic Mass The number of protons PLUS the number of neutrons 17 Cl Chlorine 35.453 17 Cl Chlorine 35.453 Atomic Number: 17 Number of Protons: 17 Number of Electrons: 17 Atomic Mass: 35 Number of Neutrons: 18 17 p+ 18 n0