* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
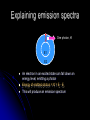
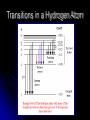
A brief history of atomic structure Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 1 Atomic Theory of matter British Chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) laid the foundations of modern atomic theory by proposing the idea of atoms. At the end of the 19th century chemists had discovered that atoms themselves were made up of smaller particles. Discovery of electrons ANODE VACCUM CATHODE • British physicist J. J. Thompson began experiments on the discharge of electricity through gases and discovered the electron. Discovery of the nucleus In 1911 British Physicist Ernst Rutherford performed the alpha particle scattering experiment Gold foil was bombarded with alpha radiation from a radioactive substance Concluded mass of an atom was concentrated in a centre, which was also positively charged An early structure for the atom Quantization of energy When heated, solids emit light. Max Planck discovered that the atoms of a solid vibrate with energy of a definite frequency, f, depending on the solid. The energy of this light is given by E = nhf, where h is Planck’s constant, 6.63 x 10-34 and n = 1, 2, 3,... This means that the energies of a vibrating atom must take the form hf, 2hf, 3hf etc. In this way thee energy said to be quantised – it cannot change smoothly from one value to another, only in whole units at a time. In 1900, Albert Einstein had proposed that instead of being thought of as a continuous wave, light could also be thought of as particles – “packets” of light – PHOTONS. Based on the theories of Einstein and Planck, Danish scientist Niels Bohr proposed a model of electronic structure to explain the results of atomic spectra. Hot gases emit light, in the form of a line spectrum Link to Periodic Table of Spectra Hydrogen Bohr’s model of the atom 4 3 1 2 3 2 E n e r g y 1 ENERGY LEVELS (SHELLS) 1. 2. An electron can only have specific energy values in an atom, ENERGY LEVELS An electron can change energy only by going from one energy level to another Explaining emission spectra One photon, hf E1 E2 An electron in an excited state can fall down an energy level, emitting a photon Energy of emitted photon = hf = Ei - Ef This will produce an emission spectrum Transitions in a Hydrogen Atom