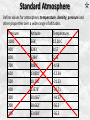
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download O 3
Precipitation wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Space weather wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Weather Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Satellite temperature measurements wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Surface weather analysis wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
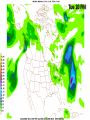
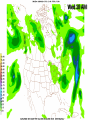
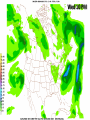
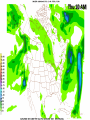
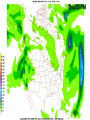
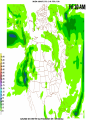
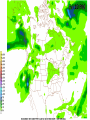
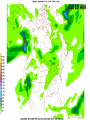
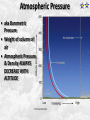
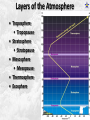
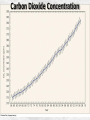
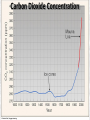
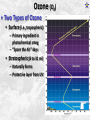
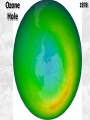
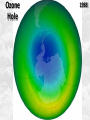
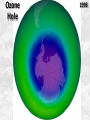
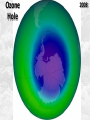
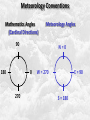
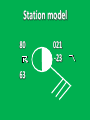
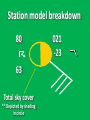
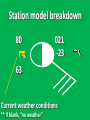
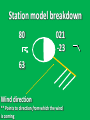
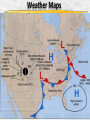
Week 2 Class Notes Tonight • Weather Review • Atmosphere (Chapter 1) • Weather Observations • Geography 101 (in class aggignment) • Weather Maps Next Week • Heat & Energy (chapter 2) • More Weather Maps Weather Review Weather Review Weather Review Weather Review Tue 10 PM Wed 10 AM Wed 10 PM Thu 10 AM Thu 10 PM Fri 10 AM Fri 10 PM Sat 10 AM Weather Songs • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • I Can't Stand The Rain Its raining man Hurricane Sun is Shining Singing in the Rain Come Clean Purple Rain I'm Only Happy When It Rains If You Steal My Sunshine Hello Sunshine Hotel California Raindrops Keep Fallin on My Head It's Raining On Prom Night Blame It On The Rain Make it Rain Ain't no Sunshine Rock You Like A Hurricane The rain song I Wish It Would Rain Stormy Weather Snowball Pennies from Heaven Five Feet High and Rising Lightning Strikes Summer Holidays in the Sun Westwind She’s like the Wind Running Against the Wind • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • The Lighthouse's Tale Winter Wonderland Rainy Day Woman Strangers in the Wind Walking On Clouds Catch the Wind Riders on the Storm Steal My Sunshine And It Rained All Night Flowers Never Bend with the Rainfall Gravity's Rainbow Hey Mr. Rain No Rain One Rainy Wish Acid Rain Drops Dust in the Wind Weather Songs • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • How I Wish it Would Rain Let it Snow You Are My Sun Shine Its Raining Men Tears and Rain Rain Stained Melodies Ain't No Sunshine No Rain Rain Down On Me Wheel in the Sky Frosty the Snow Man And it Rained All Night Rain A Hard Rains a Gonna Fall Blueberry Rain Pennies From Heaven I Can’t Stand the Rain Crooked Teeth Make it Rain Riders on the storm Let the rain fall down Rainy Days It's Raining Men Fire and Rain Texas Flood Let it Rain The Wind Cries Mary Sunday Morning Riders On the Storm Rainy Days and Mondays • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Here Comes the Sun Singing In The Rain Follow the Sun Fire and Rain Love a Rainy Night Walking On Sunshine Ain't No Sunshine My Girl Drops of Jupiter Summer Breeze Cold Day In July Stormy Weather Have You Ever Seen the Rain? It Never Rains in Southern California Raindrops Keep Falling on My Head You Are the Sunshine of My Life Over the Rainbow Rhythm of Rain Rainy Days Umbrella Blame It on the Weatherman It's Raining Men Cold Wind Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds The Rain Song Rock You Like a Hurricane I'm Praying for Rain Hurricane Pressure Zone Raining on Sunday • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • There's No Sunshine Anymore Kisses in the Rain Rihanna Umbrella Flowers Never Bend With The Rainfall Make it Rain I Can't Stand the Rain Obscured By Clouds Blame It on the Rain Sunny Rain Lightning Strikes And It Rained All Night Thunder Rolls Storm Snow Fire, Fire This Weather Itsy Bitsy Spider Electrical Storm She’s Like the Wind Pressure The Atmosphere Thin If the earth were the size of an apple, the skin would be about the same as the atmosphere. Precious Commodity • Important medium for life – Plants get most of their mass from carbon in the air – Animals rely on oxygen • Chemical composition determines – “Breathability” – Radiation balance • How much sunlight is reflected • How much sunlight is absorbed • How much outbound (thermal) radiation is absorbed Composition • Permanent and Variable Gases Particulates (Aerosols) 1 cm3 of air can contain as many as 200,000 nonO gaseous particles. 3 – – – – – – – dust dirt (soil) ocean spray volcanic ash water pollen pollutants Role of Particulates • Scattering of sunlight. • Condensation nuclei for water vapor. • Surface or catalyst for atmospheric chemistry. PM 10 and PM 2.5 • Fine Particles 10μm and 2.5μm • μm = μ = micron = micrometer • “Spare the Air” Nights • Unhealthy Air Origin of the Atmosphere Origin of the Atmosphere Primordial Atmosphere • First Atmosphere – Planet Formation: O3 Hydrogen, Helium (Methane, Ammonia) from the solar nebula (very light gasses) Secondary Atmosphere • Second Atmosphere O 3 – Volcanic Outgassing (~85% H2O, ~10% CO2, ~ SO2, ~ ash) – Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, Sulfur compounds – Nitrogen compounds – Cometary Impacts (H2O, CO2) Present Atmosphere • Third Atmosphere (present day) – Removal of Carbon Dioxide (back on the increase?) O3 • Water (Ocean stores 5 times atmosphere) • Photosynthesis • Photoplankton absorption – Nitrogen increase (breakup of nitrogen compounds by UV) – Oxygen increase (photosynthesis) Atmospheric Pressure • aka Barometric O Pressure • Weight of column of air • Atmospheric Pressure & Density ALWAYS DECREASE WITH ALTITUDE 3 Layers of the Atmosphere • Troposphere • Tropopause • Stratosphere • Stratopause • Mesosphere • Mesopause • Thermosphere • Exosphere Lower Atmosphere • Troposphere: – – – – Greek word “tropein” = change Extending to about 36,000’ (10 km.) Contains most of atmosphere and most “weather.” 80% of the atmosphere • Tropopause – isothermal layer (36,000 - 65,000’) • 99.99997% of atmosphere by mass is below 60,000’ • Stratosphere: – 65,000 -165,000’ – Temperature increase because of ozone absorption of UV – Region is very stable against vertical air motions and its structure is “stratified.” Upper Atmosphere • Mesosphere: – “Middle sphere” – 165,000’ – 295,000’ – Only 0.01% of the total atmosphere but same percentage of gases. • Thermosphere: – > 295,000’ – “Hot Layer” – Very low density and exposed to the greatest amount of solar insolation. – Changes in solar output greatly affect the temperature in the thermosphere. These changes cause the region to shrink and puff out, providing atmospheric drag on low orbit satellites in space. Higher Layers • Exosphere: The outer limits of earth’s atmosphere. – The interface between earth and space. • Ionosphere – Not a True Layer - Electrified region – Top of stratosphere through most of mesosphere – “Reflects” radio waves AM Radio and the Ionosphere AM radio absorption/reflection depends upon the ionization states of molecules in the ionosphere. Standard Atmosphere Define values for atmospheric temperature, density, pressure and other properties over a wide range of altitudes. Pressure 1000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 Altitude 364’ 3243’ 6394’ 9883’ 13,801’ 18,290’ 23573’ 30,065’ 38.662’ 53.083’ Temperature 12.28 C 8.57 2.33 -4.58 -12.34 -21.23 -31.71 -44.57 -56.5 -56.5 Primary Levels 1000 mb = Surface 850 mb = 5,000’ 700 mb = 10,000’ 500 mb = 18,000’ (middle of atmosphere) 300 mb = 30,000’ Lapse Rate • The change of temperature with altitude – Usually cools with altitude – Inversions – warming with height – Isothermal – no change with height • Approximate average lapse rate: – ~ 3.6 oF (2o C) per 1000 feet • This rate changes from day to day – Due to different airmasses – Changes in humidity. Greenhouse Gasses • CO2 – carbon dioxide • H2O - water • N2O – nitrous oxides • CH4 - methane • O3 – Ozone (insignificant) • Transparent in visible wavelengths – emitted by the sun • Absorption in the infrared wavelengths – emitted by the earth’s surface Carbon Dioxide CO2 • Sources O – vegetative decay – volcanic eruptions – animal exhalation – combustion of fossil fuels 3 • Sinks – dissolves in water – photosynthesis (oxygen production) – phytoplankton absorption (limestone formation) Carbon Dioxide Concentration Carbon Dioxide Concentration Ozone (O3) • Two Types of Ozone • Surface (i.e., tropospheric) – Primary ingredient in photochemical smog – “Spare the Air” days • Stratospheric (6 to 31 mi) – Naturally forms – Protective layer from UV Ozone Destruction • Surface Ozone Ozone Destruction • Stratospheric Ozone – UV radiation has enough energy to naturally break up the molecule. – Acclerated by CFCs’ • Hairspray, freon etc. • Catalyst • Accelerate Breakdown Ozone Destruction Ozone Hole 1978 Ozone Hole 1988 Ozone Hole 1998 Ozone Hole 2008 Meteorology Conventions Mathematics Angles (Cardinal Directions) Meteorology Angles 90 180 N=0 0 270 W = 270 E = 90 S = 180 Altitude In meteorology altitude is represented on charts as increasing upward. Altitude Temperature Time Conventions Greenwich Mean Time • GMT • UTC (Coordinate Universal Time) • Zulu (Z) • PST = UTC – 8 hours • PDT = UTC – 7 hours – 0000 UTC = 1700 PDT = 5 PM PDT – 1200 UTC = 0500 PDT = 5 AM PST WEATHER OBSERVATIONS ° What We Measure ° ° ° ° ° ° ° Cloud Cover Visibility Precipitation Winds Temperature Humidity Pressure Clouds ° Cloud Cover (Tenths of the sky) ° ° ° ° Clear < 1/10th Scattered 1/10th - 5/10th Broken 6/10th - 9/10th Overcast > 9/10th ° Cloud type ° Cloud height ° ° ° ° Ceilometer Aircraft Balloon Estimation Visibility ° Horizontal Distance ° More than 1/2 of the horizon ° Restrictions if < 7 miles ° ° ° ° ° Smoke Haze Fog Rain Snow ° Transmissometer Precipitation ° Type ° ° ° ° Rain Snow Drizzle Hail ° Amount ° Locations ° Rain gauge ° Snow stakes Tipping Bucket Raingauge Wind ° Direction ° Where wind comes from ° Compass points or degrees ° Wind vane, estimate ° Speed ° Knots or MPH ° Sustained vs Gusts ° Anemometer Temperature/ Humidity ° Temperature ° Well ventilated, shady, 5’ ° Scales: Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin ° Thermometer, Thermister ° Humidity ° ° ° ° ° Relative Humidity (%) Dew Point (F,C) Wet Bulb (F,C) Psychrometer Hygrometer Barometric Pressure ° Force of air pressing down ° Barometer ° Mercurial ° Aneroid ° Units ° Inches of Mercury ° Millibars Map Classwork Map Classwork Map Classwork Map Classwork Map Classwork Map Classwork Weather Symbols and Maps Station model 80 63 021 -23 Weather Symbols Sky Symbols Wind Symbols Pressure Tendency Station model 80 63 021 -23 Station model breakdown 80 63 Total sky cover ** Depicted by shading in circle 021 -23 Station model breakdown 80 63 Dew point temperature Surface: ºF Upper air: ºC 021 -23 Station model breakdown 80 021 -23 63 Current weather conditions ** If blank, “no weather” Station model breakdown 80 021 -23 63 Wind direction ** Points to direction from which the wind is coming Station model breakdown 80 021 -23 63 Wind speed Long barb = 10 knots Short barb = 5 knots Flag = 50 knots ** Notice range of wind speeds (i.e., 28-32 knots) Station model breakdown 80 021 -23 63 Sea level pressure **If first number is 5 or greater, then place 9 in front --Otherwise, place 10 in front **Place decimal point between last two numbers Station model breakdown 80 021 -23 63 Change in surface pressure during last 3 hours ** In tenths of mb ** Line describes how pressure changes over time from left to right Example 1 • Temperature: 76 ºF • Dew point: 65 ºF • Sky cover: Completely overcast • Current weather: Light rain • Wind direction and speed: Southwest at 15 knots • Sea level pressure: 995.3 mb • Pressure tendency: Increase of 1.6 mb; rising steadily 76 65 953 +16 Example 2 •Temperature: 10ºF •Dew point: 8ºF •Sky cover: 7/10 or 8/10 •Current weather: Snow shower •Wind direction and speed: North at 3-7 knots •Sea level pressure: 1010.5 mb •Pressure tendency: Decrease of 0.4 mb; falling, then steady 10 8 105 -4 High & Low Pressure Systems ° Air pressure Pattern is main organizing feature ° Circulation in Northern Hemisphere ° Clockwise around Highs (H) ° CCW around Lows (L) ° Clouds & Precip around Lows ° Temperature patterns result from latitude, wind flow and cloud cover Plotting Fronts ° Boundary between Different Air Masses ° Types of Fronts Weather Maps Weather Maps Weather Maps Weather Maps Weather Maps Weather Maps Weather Maps