* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction - San Jose State University
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Early 2014 North American cold wave wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
North Report wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
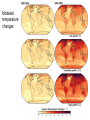
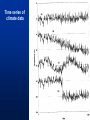
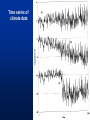
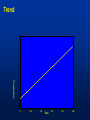
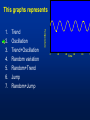
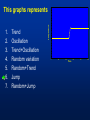
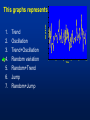
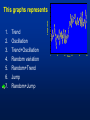
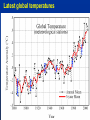
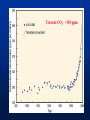
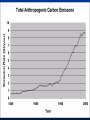
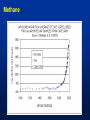
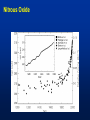
MET 112 Global Climate Change – Lecture 10 Recent Climate Change Dr. Craig Clements San Jose State University Outline Recent trends in temperature Recent trends in GHGs Time scales Modeled temperature changes IPCC (2007) (b) Additionally, the year by year (blue curve) and 50 year average (black curve) variations of the average surface temperature of the Northern Hemisphere for the past 1000 years have been reconstructed from “proxy” data calibrated against thermometer data (see list of the main proxy data in the diagram). The 95% confidence range in the annual data is represented by the grey region. These uncertainties increase in more distant times and are always much larger than in the instrumental record due to the use of relatively sparse proxy data. Nevertheless the rate and duration of warming of the 20th century has been much greater than in any of the previous nine centuries. Similarly, it is likely7 that the 1990s have been the warmest decade and 1998 the warmest year of the millennium. Time series of climate data Time series of climate data Examples of Temperature Change Trends Periodic Oscillations Random Variations Jumps Examples of Temperature Change Draw the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Trend Oscillation Trend + Oscillation Random variations Random + trend Jump Random + jump Trend Temperature 0 20 40 Time 60 80 100 This graphs represents Trend Oscillation Trend+Oscillation Random variation Random+Trend Jump Random+Jump Temperature 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 0 20 40 Time 60 80 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Trend Oscillation Trend+Oscillation Random variation Random+Trend Jump Random+Jump Temperature This graphs represents 0 20 40 Time 60 80 100 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Trend Oscillation Trend+Oscillation Random variation Random+Trend Jump Random+Jump Temperature This graphs represents 0 20 40 Time 60 80 100 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Trend Oscillation Trend+Oscillation Random variation Random+Trend Jump Random+Jump Temperature This graphs represents 0 20 40 Time 60 80 100 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Trend Oscillation Trend+Oscillation Random variation Random+Trend Jump Random+Jump Temperature This graphs represents 0 20 40 Time 60 80 100 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Trend Oscillation Trend+Oscillation Random variation Random+Trend Jump Random+Jump Temperature This graphs represents 0 20 40 Time 60 80 100 Time Frames -- Examples Seconds to minutes – Small-Scale Turbulence Hours – Diurnal Cycle (Caused by Earth’s Rotation) Hours to Days – Weather Systems Months – Seasonal Cycle (Caused by tilt of axis) Years – El Niño Decades -- Pacific Decadal Oscillation Centuries – Warming during 20th Century (Increase in greenhouse gases?) Tens of thousands of Years – Irregularities in Earth’s motions Millions of Years – Geologic Processes Latest global temperatures …“Over the last 140 years, the best estimate is that the global average surface temperature has increased by 0.6 ± 0.2°C” (IPCC 2001) So the temperature trend is: 0.6°C ± 0.2°C What does this mean? Temperature trend is between 0.8°C and 0.4°C The Uncertainty (± 0.2°C ) is critical component to the observed trend Current CO2: ~383 ppm What Changed Around 1800? Industrial Revolution – Increased burning of fossil fuels Also, extensive changes in land use began – the clearing and removal of forests Burning of Fossil Fuels Fossil Fuels: Fuels obtained from the earth are part of the buried organic carbon “reservoir” – Examples: Coal, petroleum products, natural gas The burning of fossil fuels is essentially – A large acceleration of the oxidation of buried organic carbon Land-Use Changes Deforestation: – The intentional clearing of forests for farmland and habitation This process is essentially an acceleration of one part of the short-term carbon cycle: – the decay of dead vegetation Also causes change in surface albedo (generally cooling) Carbon Budget Changes Units in Peta-grams (x1015) of Carbon per year (PgC/yr) Atmosphere increase 3.3 ± 0.1 – Observations Emissions (fossil fuel, cement) 5.4 ± 0.3 – Estimates from industry Ocean-atmosphere flux -1.9 ± 0.6 – Estimates from models/obs Final component is Land/atmosphere flux: What is the land/atmosphere flux? Methane Anthropogenic Methane Sources Leakage from natural gas pipelines and coal mines Emissions from cattle – Flatulence…gas Emissions from rice paddies Nitrous Oxide Anthropogenic Sources of Nitrous Oxide Agriculture CFCs CFC-11 CFC-12 Sources of CFCs Leakage from old air conditioners and refrigerators Production of CFCs was banned in 1987 because of stratospheric ozone destruction – CFC concentrations appear to now be decreasing – There are no natural sources of CFCs Lecture on ozone depletion to follow later in semester… Activity 1. Describe the 120 year temperature records in terms of the seven above described types of variations (trend, trend+oscillation etc.) by breaking up the time series into periods (i.e. from 1930-1950, oscillation + positive trend, from 1950-1970, negative trend) 2. Based on the past 120 years of globally averaged temperatures: a. What trend would you assign to this period. (i.e. 0.3°C over 120 years) b. If you were to break up the data into time sections provide trends over the following time periods i) 1880-1920; b) 1920-1940 and c) 1970-2000 Temperature over the last 10 years The Land and Oceans have both warmed Precipitation patterns have changed