* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change Science and Engineering
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Energiewende in Germany wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
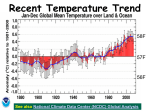
CE 401 Climate Change Science and Engineering solar input, mean energy budget, orbital variations, radiative forcing 20 January 2011 any questions from last time? we got into solar inputs and Earth radiation budget HW 2 is due today – will go over briefly on Tuesday HW 3 is posted on the web - due Tuesday 1/25 HW 4 is posted on the web – due Thursday 1/27 energy radiated to space is = s 4p R2 Te4 [the Stefan-Boltzmann law] where s = Stefan-Boltzmann constant = 5.67 x 10-8 [w m-2 K-4] 342 w m-2 is the average energy input to the Earth system 242 w m-2 is the average radiated energy from the Earth system, all radiated in the infrared part of the spectrum radiative forcing: IPCC “Radiative forcing is a measure of the influence a factor has in altering the balance of incoming and outgoing energy in the Earth-atmosphere system and is an index of the importance of the factor as a potential climate change mechanism. In this report radiative forcing values are for changes relative to preindustrial conditions defined at 1750 and are expressed in watts per square meter (W/m2)” RF can be used to estimate a subsequent change in equilibrium temperature (DT) since temperature must be related to change in radiation (linear or ??): DT = l DF where DF is the radiative forcing (W m-2), and l is called the mean climate sensitivity factor [°C/(W m-2)] and allows computation of impacts on temperature of different GHG different atmospheric models different values of l RF for CO2, l = 0.71 °C/W m-2 for a 1°C atmospheric temperature change, DF = 1.41 W m-2 factors that influence the radiative equilibrium of the Earth system average solar input: 342 w/m2 source IPCC 2007 global warming potential (GWP) of a gas GWPg: a weighting factor to compare the GHG efficiency of a gas relative to CO2. Compares potency of GHG to that of CO2: GWPg = Fg x Rg(t) dt / F CO2 x RCO2 dt where the integral is from time 0 to time T Fg = radiative forcing efficiency of the gas in question [w m-2 kg-1] FCO2 = radiative forcing efficiency of CO2 [w m-2 kg-1] Rg = fraction of the 1 kg of gas remaining in the atmosphere at time t RCO2 = fraction of the 1 kg of CO2 remaining in the atmosphere at time t radiative forcing efficiency is usually an exponential decay function, or ~ constant with time, depending on the gas. For CO2 the decay is rapid the first few decades as the biosphere absorbs the carbon, then it decays at a much slower rate corresponding to the slow CO2 uptake of the oceans Choice of time horizon for GWP depends on what a policy maker is interested in e.g. CH4 GWP is 62 for 20 yr horizon, 23 for 100 yr, and 7 for 500 yr compare CO2 to CH4 and N2O emissions for warming potential: emissions: CO2 = 27,000 MMt CO2/yr US emissions CH4 = 370 MMtCH4/yr N2O = 6 MMt N2O/yr [MMt = million metric tons] compare impacts to CO2: CH4: GWP100 = 23*370 = 8510 MMtCO2 equivalent N2O: GWP100 = 296*6 = 1776 MMtCO2 equivalent details of greenhouse gases radiation of the Earth at equilibrium effective temperature of 288K = +15°C peak of the radiation curve at about 15 µm this curve is the Planck curve for a black body at 288K CO2 as a molecular absorber H2O as a molecular absorber O3 as a molecular absorber CH4 as a molecular absorber blow up the CO2 graph to see what the absorbance looks like blow up the CO2 graph to see what the absorbance looks like rotational spectral lines of CO2 blow up the CO2 graph to see what the absorbance looks like two spectral features of CO2 molecular spectral “lines” are caused by quantized rotational energy transitions – changing energy states due to different rotational states of the atoms quantized spectra showing lines at different energies (energy proportional 1/wavelength). In the IR, different sets of rotational spectra are seen at different quantized levels of vibrational energy states of the molecule diatomic molecule – two atoms rotating, vibrating, and with electron energy transitions – all quantized so if the energy levels are quantized (monochromatic), there shouldn’t the spectral lines be monochromatic and thus have no spectal width in wavelength (energy) space? Obviously the molecular lines DO have some energy width – why? The ability of the molecule to absorb in the atmosphere depends on its quantum structure the intrinsic ability to absorb energy (light) and the abundance of the molecule in the atmosphere. The ability of an IR molecular absorber to be a greenhouse gas depends on the two parameters above, and also how the spectrum lines up with the Earth IR radiation curve. Note that there is a huge CO2 molecular band located nearly at the peak intensity of the Earth radiation curve the molecules absorb light (energy) from the Earth, change quantum state to a higher energy level, and radiate that energy into all directions statistically. The radiation from the Earth is moving skyward, after absorption and re-emission, it is moving in any direction a net drop in outward moving energy the temperature of the radiating body must increase in order to establish an equilibrium with incoming radiation from the sun. • astronomical forces also drive global climate change • seasons are driven by astronomical causes, as is the 24 h day/night cycle Earth orbital changes that vary the solar input and cause the ice ages: the Milankovich cycles – these cycles change the solar input to the Earth system eccentricity changes varies from nearly circular to high eccentricity 0.058 with mean 0.028. Caused by perturbations from the other planets e = 0.017 currently shape of earth’s orbit changes during a cycle of about 100,000 years axial tilt (obliquity) – increased obliquity increased seasonal amplitude change axis of rotation changes from about 21.5° to 24.5° --> seasonal variations over a period of 41,000 years. Tilt is the most significant cause of seasonal temp change. Modulates the seasons, does not change climate overall axial precession – trend in direction of axis of rotation in inertial space – gyroscopic motion the earth’s rotation axis precesses (wobbles) with a period of about 26,000 years due to tidal forces exerted by sun and moon on solid Earth since Earth is not spherical affects climate extremes problems with the Milankovitch theories: • 100,000 yr problem: eccentricity variations should have a smaller impact that the other mechanisms, but this is the strongest climate signal in the data record • 400,000 yr problem: eccentricity variations also show a 400,000 yr cycle but that cycle is only visible in climate records > 1My ago • observations of climate changes show behavior much more intense than calculated • the 23,000 yr cycle dominates, the opposite of what is observed • so the explanation is not 100% - there are still issues with the explanation deg change obliquity=axial tilt long of perihelion precession index calc. insolation to TOA Benthic and Vostok ice cores