* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diseases 3rd
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
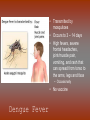
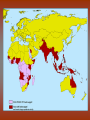
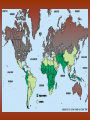
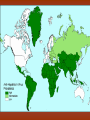
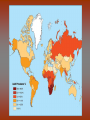
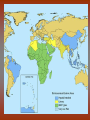
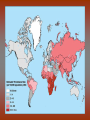
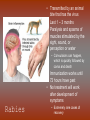
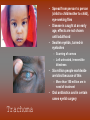
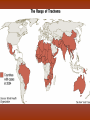
Diseases in Africa • Caused by mosquito bites • People experience fever, chill, headaches, and flu-like illness • Each yeah, 350-500 million cases occur – Over one million die – Most are children in SubSaharan Africa • Could be prevented by using bednets (preferably insecticide treated), insecticides, wearing clothes that cover most of the body, or antimalarial drugs – But no specific vaccine • Can develop in 7 days or several months Malaria Countries in Africa Afflicted with Malaria All countries south of the Sahara • Caused by mosquito bites • Range from self-limited fever to severe hepatitis and a fever that causes blood discharge • No specific treatment • Fatality rate = 20% Yellow Fever Countries Angola Benin Burkina Faso Burundi Cameroon Central Africa Republic Chad Cote d’Ivoire Democratic Republic of the Congo Equatorial Guinea Kenya Ethiopia Liberia Gabon Mali The Gambia Mauritania Ghana Niger Guinea Nigeria Guinea-Bissau Rwanda Sierra Leone Sao Tome and In SubPrincipe Senegal Saharan Somalia Africa Sudan Tanzania Togo Uganda • Transmitted by mosquitoes • Occurs to 3 – 14 days • High fevers, severe frontal headaches, joint/muscle pain, vomiting, and rash that can spread from torso to the arms, legs and face – Occasionally • No vaccine Dengue Fever • Spread by eating food/beverages that is contaminated with Salmonella Typhi (S. Thyphi) • Persistant high fever (103 – 104), headache, anorexia, rash spots • 22 million cases a year – 200,0000 die a year • Two vaccines – Oral live (capsule) – Shot – Protect 50%-80% of people Typhoid Fever • Spread by contaminated food, fecal contamination in water • Watery diarrhea, vomiting, circulatory collapse – Leads to rapid loss of body fluids – Without treatment, death can occur in hours • Two oral vaccines (not available in the US) • Rehydration is main treatment – Oral rehydration salts Cholera A B • Viral infection of the liver • Fever, anorexia, nausea, malaise • Can be transmitted by direct person-to-person contact, contaminated water/food, uncooked food • Two vaccines • Fever, anorexia, malaise, nausea • Transmitted by unprotected sex with a HBV infected partner, contaminated needles used for injection of drugs/hospitals, unscreened blood transfusions • Two Vaccine – Both shots Hepatitis – Both shots • HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) • AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) • Damages the immune system (which allow certain cancers to develop) • Transmitted by sexual contact, using contaminated syringes, using infected blood – Many women with child bearing HIV will pass it to the infant AIDS/HIV • Recognized in 1981 • Nearly 40 million people are affected worldwide • Spread by larvae from infected snails that can penetrate unbroken skin, brief exposure to contaminated water • Fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, weakness/joint and muscle pain, diarrhea, nausea – Few cases produce seizures or disease in the liver, kidney, lung, intestinal tract, and bladder • No vaccine Schistosomiasis • Transmitted airborne (person infected coughs and spreads to other people in the same space) – The germs can stay in the air for hours depending on the environment • Weight loss, fever, night sweats, chest pain, coughing of blood • Affects the lungs, brain, or spine • Take several drugs for 6 – 12 months Tuberculosis – If directions are not specifically followed, person could become sick again or resistant to the drug • Transmitted by an animal bite that has the virus • Last 1 – 3 months • Paralysis and spasms of muscles stimulated by the sight, sound, or perception or water – Convulsions can happen, which is quickly followed by coma and death • Immunization works until 72 hours have past • No treatment will work after development of symptoms Rabies – Extremely rare cases of recovery • Spread from person to person (child to child/mother to child), eye-seeking flies • Disease is caught at an early age, effects are not shown until adulthood • Swollen eyelids, turned-in eyelashes – Scarring of cornea – Left untreated, irreversible blindness • Six million people worldwide are blind because of this – More than 150 million are in need of treatment • Oral antibiotics and in certain cases eyelid surgery Trachoma