* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infectious Disease Summary
History of biological warfare wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
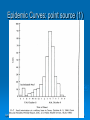
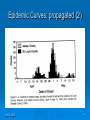
Infectious Disease Summary N. Birkett, Back-to-Basics, 2008 Terminology Nature of diseases Outbreaks/epidemics Identification Methods of control April 3, 2008 1 April 3, 2008 2 Terminology (1) Infectivity The ability of an agent to invade and multiply in a host (an infection). Dose of organism required to establish infection in 50% of animals. Pathogenicity The ability of an agent to produce clinically apparent illness. April 3, 2008 3 Terminology (2) Virulence The proportion of clinical cases which produce severe disease and/or permanent sequelae. Immunogenicity The ability of an agent to produce specific immunity against the agent Can be produced in general body or within specific sites such as the GI tract. Determines the ability of an agent to re-infect a host • Measles vs. gonorrhea April 3, 2008 4 Terminology (3) RESERVOIR FOMITES (Vehicle) Living organisms or inanimate matter in which infectious agent normally lives and multiplies Inanimate objects contaminated with infectious agent (not the reservoir). Example would be toys in a daycare centre. VECTOR An animate source of an infectious agent. The vector may be infected with the organism (e.g. mosquitoes and malaria) or just be a mechanical carrier (e.g. flies). There is disagreement about whether vectors are restricted to insects or can also include small mammals. April 3, 2008 5 Terminology (4) ZOONOSES CARRIERS Diseases transmitted to humans from animals (e.g. anthrax) An infected person without apparent clinical disease who remains infectious (e.g. Typhoid Mary) INDEX CASE The person (case) who brings the infection to the attention of the medical community or the public agency. Sometimes used to refer to the person who brings the infection into a community. This will often (but not always) be the same person. April 3, 2008 6 Terminology (5) ATTACK RATE The probability that people will get ill from the disease. Usually applied in an outbreak situation. # new cases in group # people in group SECONDARY ATTACK RATE Probability of infection in a closed group who are at risk but excluding the index case(s). Formula is: April 3, 2008 # new cases in group - index case(s) # people in group - index case(s) 7 Terminology (6) CASE FATALITY RATE The probability of death in people with an infection. April 3, 2008 8 April 3, 2008 9 April 3, 2008 10 April 3, 2008 11 Pathogenic Mechanisms (1) Direct Tissue Invasion Production of Toxins Allergic Host Reaction Resistant/latent infection (carriers) Enhancement of host susceptibility to drugs (e.g. Reye’s syndrome and ASA). Immune Suppression April 3, 2008 12 Reservoirs (examples of transmission patterns) Human Human Human Animal Animal Human Animal Animal Vector Vector Human April 3, 2008 13 Epidemics (1) Epidemic (now often called ‘outbreak’) Endemic the occurrence of a disease/condition at a relatively constant level in a given setting Pandemic the occurrence in a community or region of cases of a disease/condition/behaviour clearly in excess of normal expectancy an epidemic covering a very wide area and affecting a large proportion of the population Pathogen Infectious and non-infectious substance capable of producing tissue damage or initiating a process which can lead to a disease. April 3, 2008 14 Epidemics (2) Common conditions increasing likelihood of an epidemic The introduction of a new pathogen or an increased amount of, or a change in the virulence of, a pathogen. An adequate number of exposed and susceptible persons. An effective means of transmission between the source of the pathogen and the susceptible person. April 3, 2008 15 Epidemics (3) Incubation period and causal agent Time frame Examples Hours Food toxins Heavy metals Days Bacterial infections Salmonella / cholera Weeks Measles / mumps / Hep A Months Hep B / Rabies Years Kuru / cancer April 3, 2008 16 Epidemics (4) Types of epidemics Common source • Point source • Ongoing exposure • Need not be geographically localized Propagated/progressive Mixed Epidemic curve Spot maps Note that epidemics can arise from behaviour as well as from traditional infectious sources. April 3, 2008 17 Epidemic Curves: point source (1) April 3, 2008 18 Epidemic Curves: propagated (2) April 3, 2008 19 Factors Influencing Spread of Disease in a Population (1) Period of infectivity in relationship to symptoms Includes consideration of carrier states Herd immunity Type of spread Person to person Common vehicle Vector-borne Zoonoses Transmission mechanics Consider sexual vs. droplet spread April 3, 2008 20 Herd Immunity April 3, 2008 21 Epidemics (6) Two strategies to control disease spread Isolation • Separation of infected persons or animals from other susceptible people/animals during the period of communicability. Quarantine • Restrictions on the activities of well people who have been exposed to a communicable disease, during its period of communicability. Immunization Chemoprophylaxis April 3, 2008 22