* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diseases/Disorders of the Nervous System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
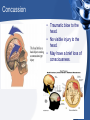
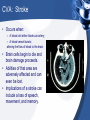
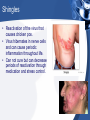
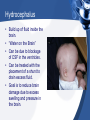
Diseases/Disorders of the Nervous System Categories of Conditions • • • • • Trauma Structural abnormalities Degenerative Infectious Mental Health Concussion • Traumatic blow to the head. • No visible injury to the head. • May have a brief loss of consciousness. CVA: Stroke • Occurs when: – A blood clot either blocks an artery; – A blood vessel bursts; altering the flow of blood to the brain. • Brain cells begin to die and brain damage proceeds. • Abilities of that area are adversely affected and can even be lost. • Implications of a stroke can include a loss of speech, movement, and memory. Categories of Conditions • • • • • Trauma Infectious Structural abnormalities Degenerative Mental Health Infections • Encephalitis – Inflammation of the brain. – Usually caused by a virus. – Symptoms include: • Flu-like symptoms • Headache • Irritability • Lethargy • Seizures • Body aches and pains • Meningitis – Inflammation of the meninges; – Caused by bacteria, virus, or fungus. – Symptoms include: • Photophobia • Headache • Stiff neck • Nausea • Vomiting • Fever Shingles • Reactivation of the virus that causes chicken pox. • Virus hibernates in nerve cells and can cause periodic inflammation throughout life. • Can not cure but can decrease periods of reactivation through medication and stress control. Categories of Conditions • • • • • Trauma Infectious Structural abnormalities Degenerative Mental Health Epilepsy • Recurring seizure episodes due to abnormal over-activity of neurons. • Cause is unknown; can be controlled through medication. • Can exhibit as: – Grand mal: convulsive seizures – Petit mal: absence seizures. Hydrocephalus • Build up of fluid inside the brain. • “Water on the Brain” • Can be due to blockage of CSF in the ventricles. • Can be treated with the placement of a shunt to drain excess fluid. • Goal is to reduce brain damage due to excess swelling and pressure in the brain. Categories of Conditions • • • • • Trauma Infectious Structural abnormalities Degenerative Mental Health Alzheimer’s Disease • Progressive, fatal brain disease. • Most common form of dementia. • Progressive loss of cerebral brain matter due to build up of abnormal proteins. • Affects up to 5 million Americans. Parkinson’s Disease • Gradual degeneration of nerve cells that control body movement. • Typically begins in late 50’s, early 60’s. • More common in men than women. • Initial symptoms include: – Weakness – Trembling – Numbness Multiple Sclerosis • Results from loss of insulation (demyelination) of motor nerve fibers. • Progressive loss of motor function. • Initial symptoms include: – Weakness – Headaches – Trembling – Vision loss Cerebral Palsy • Abnormalities in parts of the brain that control muscle movement and coordination. • Can occur due to problems during pregnancy and/or delivery. • Signs usually appear before the age of three. • Can affect muscle movement, hearing, vision, learning, and speech. • Symptoms include: – Stiff/tight muscles – Spasticity in movement – Lack of muscle tone. Categories of Conditions • • • • • Trauma Infectious Structural abnormalities Degenerative Mental Health Tourette Syndrome • an inherited neuropsychiatric disorder • Typical onset in childhood • Characterized by multiple physical (motor) tics and at least one vocal tic. • Tics characteristically wax and wane. • Can be suppressed temporarily, and are preceded by an urge to tic. • Video link 1:00:00 Schizophrenia • Disturbance in thinking, emotional reactions, and social behavior. • Results in chronic illness and personality changes leading to hallucinations, delusions, and apathy. • Affects about 2 millions Americans. • Diagnosed between 15 and 25 years of age. • Treated with behavior modification and medications. OCD • Obsessive Compulsive Disorder • Affects 3.3 million American adults • Ritual or repetitive behaviors that interfere with a person’s ability to concentrate, function at work, or interact in social situations. • Can be treated with medications and behavior therapy. Depression • Feelings of hopelessness, sadness, pessimism, and loss of interest in life. • Most common mental health disorder. • Affects 9.8 million Americans age 18 and older. • 80% responds to medications and psychotherapy. • Causes are typically biological/chemical and environmental. Other Nervous System Conditions • Headaches • Phobias • Primary brain cancer • Addiction • Huntington’s disease • Autism • Anxiety • Lou Gehrig’s Disease • ADD/ADHD • Dyslexia • Bipolar Disorder • Pain • Neurological AIDS • Neurological Syphilis • And more….