* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cardiovascular System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
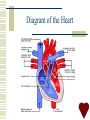
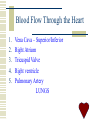
The Cardiovascular System Learning Outcome Show an understanding of the cardiovascular system Describe the structure and function of the heart Describe the major components of the circulatory system Cardiovascular System Consists of Heart, Lungs and Vessels BODY HEART Systemic circulation LUNGS Pulmonary Circulation The Heart Made of cardiac muscle (myocardium) Has it’s own blood supply Two upper thin walled chambers – atria Two lower thick walled chambers – ventricles Atria collect blood from the body – attached to veins Ventricles send blood to the body – attached to arteries The Heart Right side – deoxygenated Left side – oxygenated Separated by a thick walled septum Right atrium and ventricle connected by tricuspid valve Left atrium and ventricle connected by bicuspid (mitral) valve Cuspid valves held shut by Chordae Tendinae Left ventricle is thicker than the right Vessels of the Heart Pulmonary artery* Pulmonary vein Superior and Inferior Vena cava Aorta* *Semi-lunar valves Diagram of the Heart Blood Flow Through the Heart 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Vena Cava – Superior/Inferior Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Right ventricle Pulmonary Artery LUNGS Blood Flow Through the Heart 6. Pulmonary veins 7. Left Atrium 8. Bicuspid/Mitral/Atrioventricular valve 9. Left Ventricle 10. Aorta MAJOR ORGANS Control of the Heart Myogenic-Initiated from inside the heart as opposed to nervous stimulus outside Initial Stimulus originates in the Sinoatrial node (SA node) *show location Pacemaker determines heart rate Wave of excitation across both atria causes them to contract Control of the Heart Sinoventricular node (SV node) Sends waves of excitation along Purkinje Fibres which collectively make up the Bundle of Hiss. Along septum, radiate upwards Ventricles contract Both atria and both ventricles contract at the same time Systole-contraction of heart Diastole-Relaxation/filling of the heart Diagram On Board Vessels of the Cardiovascular System Arteries – Arterioles – Capillaries - Venules Veins Different structures and functions Arteries Carry blood Away from the heart, generally oxygenated there are some exceptions. Blood in arteries in under high pressure Their structure is related to their function Round in structure with relatively thick walls composed of three layers Arteries A. Tunica Intima – Single layer of endothelial cells B. Tunica Media – A thick layer containing elastic fibres and muscle tissues. Closer to heart more elastic fibres those further away have more muscle fibre C. Tunica Externa – Contains collagen fibres for strength Diagram of an Artery Veins Carry blood back to the heart (generally deoxygenated) Blood now flowing slowly, smoothly and under low pressure (structure related to this function) Walls are relatively thin compared with arteries Still same three layers but the tunica media differs in size – relatively narrow with few muscle fibres and elastic fibres Semi Lunar valves present along length Diagram of Veins Capillaries Link the arterial and venous blood supplies Blood flow is slow, blood pressure is falling and is non-pulsatile Capillaries form vast networks in all tissues and organs Composed of only the Tunica Intima, only a single layer of endothelial cells, no elastic fibres and no muscle tissue Capillaries Exchange of materials between the blood and the body takes place in the capillary bed Diagram of a capillary bed. Diagram of a Capillary