* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
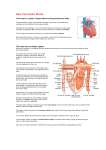
REVISION – CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Match the word/s with the definition: Word Definition The contraction phase of the atria and ventricles. It can be measured in mmHg and gives the upper reading of BP The two lower chambers of the heart. The left one pumps blood to the body via the aorta and the right one pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery. The pressure wave that results from the thrust that occurs when the ventricles of the heart contract. It is normally measured at the wrist or neck. Major organ of the body which is responsible for pumping blood around the body. Consists of four chambers and divided into two halves by the septum. Major artery of the body which carries oxygenated blood out of the left ventricle and through the systemic circulatory system Shaped like a bi-concave disc, contain iron, have a life-cycle of about 120 days and produced in bone marrow. Contain haemoglobin (Hb) Microscopically thin blood vessels which are fed by arterioles and are semipermeable, allowing O2 and CO2 to pass through their walls Found in the heart between the top and bottom chambers. Prevent regurgitation of blood. During exercise the muscles surrounding the veins expand and contract, pressing on the veins & causing a pumping effect to maintain venous return This artery takes de-oxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs to pick up O2 and get rid of CO2. Number of times the heart beats per minute. Can increase due to: fear, excitement, exercise, ingestion of food, smoking and taking drugs. These are produced in the bone marrow, lymph tissue and spleen. They have no special shape. These are responsible for clotting of blood and are formed in the bone marrow. These carry blood at high pressure away from the heart and are three layers thick. The middle (muscle) layer is thick and allows for expansion. Type of muscle that forms the heart. It receives its own nourishment via the coronary arteries The valve in the heart that has three cusps and opens when the right atrium contracts and pushes blood into the right ventricle Amount of blood ejected by the left ventricle each minute. At rest, usually about 5 litres/minute. A condition where a person has a shortage of red blood cells and constantly feels tired, weak and breathless This cardiac parameter changes throughout the day. It tends to be lower during sleep. The upper reading can rise after meals. These have thinner walls than arteries and are less elastic. Blood has to travel against gravity and back up to the right atrium. Valves Skeletal pump Ventricles Pulmonary Cardiac output Tricuspid Arteries Anaemia Blood pressure Capillaries Veins Systole Red blood cell Pulse Cardiac White blood cell Aorta Platelets Heart rate Heart