* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9 The Circulatory System
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
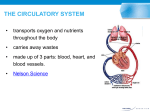
The Circulatory System A. Introduction 1. Purpose of the circulation 2. ~9% of population die from cardiovascular diseases 3. Components of the system a. Cardiovascular system = blood, vessels, heart b. Lymphatic system = lymph, vessels, lymphoid organs 4. General route of the circulation The Circulatory System B. Blood 1. Formed elements a. Erythrocytes (red blood cells, RBCs) i. Not a true cell ii. Hemoglobin b. Leukocytes (white blood cells, WBCs) (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, lymphocytes) c. Thrombocytes (platelets) 2. Plasma = 91.5% water, 8.5% solutes The Circulatory System C. Heart 1. Location 2. Endocardium, myocardium (heart muscle), epicardium a. Atrial muscle mass b. Ventricular muscle mass c. Cardiac skeleton The Circulatory System C. Heart 3. Chambers a. Right and left atrium b. Right and left ventricle c. Interatrial septum d. Interventricular septum 4. Valves a. Atrioventricular (AV) valves i. Tricuspid ii. Bicuspid (mitral) b. Semilunar valves The Circulatory System C. Heart 5. Great vessels a. Superior vena cava b. Inferior vena cava c. Pulmonary trunk right and left pulmonary arteries d. Pulmonary veins e. Aorta The Circulatory System C. Heart 6. Coronary arteries right coronary artery left coronary artery circumflex artery marginal artery posterior interventricular artery anterior interventricular artery (left anterior descending a.) The Circulatory System C. Heart 7. Conduction system 8. Cardiac cycle Arrows indicate direction of conduction sinoatrial node atrioventricular node a. Systole b. Diastole left bundle branch 9. Cardiac output a. CO = SV x HR b. ~5 L/min 10. Cardiac reserve AV bundle right bundle branch Purkinje fibers The Circulatory System D. Blood vessels 1. Structure a. Tunica intima (endothelium) b. Tunica media c. Tunica adventitia 2. Organization a. Heart arteries arterioles b. Capillaries c. Venules veins with valves heart The Circulatory System E. Lymphatic system 1. Organization a. Lymph lymphatic capillaries b. Lymphatic vessels lymph nodes c. Lymph ducts back to the blood 2. Organs = bone marrow, nodes, thymus, spleen 3. Functions a. Return tissue fluid to blood b. Production of lymphocytes = immunity c. Absorption of dietary lipids The Circulatory System F. Age-related changes 1. Blood a. No major changes b. Total volume begins to decrease >80 c. Hematocrit and hemoglobin decrease >65 d. Plasma proteins tend to decrease, but fibrinogen (major clotting factor) tends to increase by 25% >70 e. Red marrow replaced by yellow marrow; new blood cell formation may decrease The Circulatory System F. Age-related changes 2. Heart a. Slight reduction in size b. General decrease in size and number of myocardial cells, with some loss in strength c. Increased fat deposition on heart surface d. Lipofuscin accumulation in myocardial cells e. Endocardium and valves thicken and may sclerose The Circulatory System F. Age-related changes 2. Heart f. Increase in elastin and reticular fibers, and fat, within cells of the conduction system g. Maximum oxygen consumption value begins to fall at 30; may be 40% reduction by 65 h. Heart rate decreases i. Cardiac output and cardiac reserve decrease The Circulatory System F. Age-related changes 3. Blood vessels a. Loss of arterial elasticity (50% reduction >70) b. Increased collagen in walls of arterioles c. Narrowing of vessel internal diameters by gradual accumulation of lipid d. Venous walls thicken and calcify in spots e. Peripheral resistance gradually increases as a result of these changes f. Increased blood pressure The Circulatory System G. Age-related dysfunctions 1. Atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis a. Plaque formation due to excess LDLs i. Common locations ii. Plaques narrow vessel diameters iii. Promote clot formation iv. Arteriosclerosis formation b. Effects of smoking and coffee c. You can’t escape your heredity The Circulatory System G. Age-related dysfunctions 2. Hypertension (pre = 130/80) (stage 1 = 140/90) a. Incidence increases with age (30% >65) b. Causes c. Effects i. Heart attack ii. Heart failure iii. Kidney failure iv. Rupture of blood vessels The Circulatory System G. Age-related dysfunctions 3. Coronary artery disease a. Insufficient blood flow to cardiac muscle b. Leads to ischemic heart disease c. Normally, 65% maximum coronary blood flow at age 65 d. Atherosclerosis is #1 cause e. Treatment options The Circulatory System G. Age-related dysfunctions 4. Angina pectoris a. Pain related to cardiac ischemia b. Result of progressively constricted coronary arteries c. Usually atherosclerosis-induced d. Occurs with exertion e. Always a harbinger of impending heart attack f. Treatments The Circulatory System G. Age-related dysfunctions 5. Myocardial infarction (heart attack) a. Result of coronary artery blockage b. What is an infarction? c. Three zones of damage d. Effects i. Decreased cardiac output = decreased blood pressure ii. Venous accumulation of blood = pulmonary edema The Circulatory System G. Age-related dysfunctions 6. Cardiac dysrhythmias a. Irregular heartbeats b. More common with age c. Not necessarily pathological d. Bradycardia vs. tachycardia e. Flutter vs. fibrillation f. Results g. Treatments The Circulatory System G. Age-related dysfunctions 7. Congestive heart failure a. AKA = cardiac insufficiency – heart unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s need b. If the left heart doesn’t pump out what it gets in, there is a damming effect in the lungs c. If the right heart doesn’t pump out what it gets in, there is a damming effect in the systemic veins d. Relationship to kidney function e. Treatments The Circulatory System H. Take home messages 1. No changes in volume, composition, or components of blood with aging 2. Heart enlarges and weakens as a result of CV disease 3. Blood pressure increases, while stroke volume, maximum heart rate, cardiac output, and cardiac reserve decrease 4. Valves thicken and calcify 5. Decreased elasticity of blood vessels end