* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Valvular Heart Disease/Myopathy/Aneurysm
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
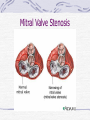
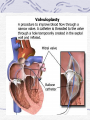
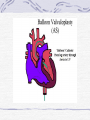
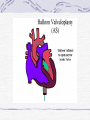
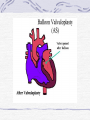
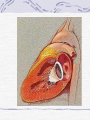
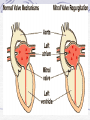
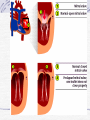
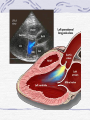
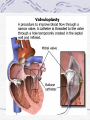
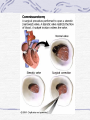
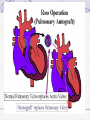
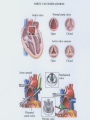
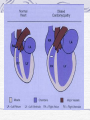
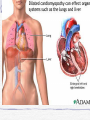
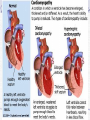
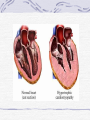
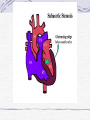
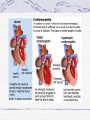
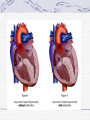
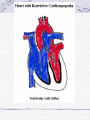
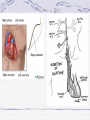
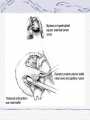
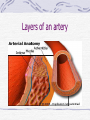
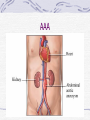
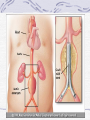
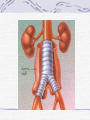
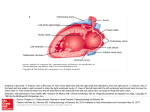
Valvular Heart Disease/Myopathy/Aneurysm Valvular Heart Disease HeartPoint: HeartPoint Gallery http://www.heartcenteronline.com/myheartdr/co mmon/articles.cfm?ARTID=187 Risk Factors Rheumatic Heart Disease MI Congenital Heart Defects Aging CHF Pathophysiology Stenosis- narrowed valve, increases afterload Regurgitation or insufficiency- increases preload. The heart has to pump same blood **Blood volume and pressures are reduced in front of the affected valve and increased behind the affected valve. This results in heart failure All valvular diseases have a characteristic murmur murmurs Mitral Valve Stenosis Mitral Stenosis Dec. flow into LV LA hypertrophy Pulmonary pressures increase Pulmonary hypertension Dec. CO * early symptom is DOE Later get symptoms of R heart failure A fib is common- anticoagulants Usually secondary to rheumatic fever Mitral Regurgitation Regurg of blood into LA during systole LA dilation and hypertrophy Pulmonary congestion RV failure LV dilation and hypertrophy-to accommodate inc. preload and dec CO Mitral Valve Prolapse A type of mitral insufficiency Usually asymptomatic May get atypical chest pain related to fatigue Tachydysrhythmias may develop Risk for endocarditis is increased and need prophylactic antibiotics A&P 1 Heart part 1 Aortic Stenosis Increase in afterload Reduced CO LV hypertrophy Incomplete emptying of LA Pulmonary congestion RV strain Symptoms Syncope Angina Dyspnea Aortic Stenosis May be asymptomatic for many years due to compensation DOE, angina, and exertional syncope are classic symptoms Later get signs of R heart failure Untreated-poor prognosis- 1020%sudden cardiac death Aortic Regurgitation Get increased preoad- 60% of SV can be regurgitated Characteristic water hammer pulse Regurgitation of blood into the LV LV dilation and hypertrophy Dec. CO Water Hammer pulse Pulse, water hammer: A jerky pulse that is full and then collapses because of aortic insufficiency (when blood ejected into the aorta regurgitates back through the aortic valve into the left ventricle ). Also called a Corrigan pulse or a cannonball, collapsing, pistol-shot, or trip-hammer pulse. Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disorders Result in R side heart failure Diagnostic Tests Echo- assess valve motion and chamber size CXR EKG Cardiac cath- get pressures Medications Like Heart Failure ACE, Dig Diuretics Vasodilators Beta blockers Anticoagulants *Prophylactic antibiotics Medical/ Surgical Treatment Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty Surgery Open commissurotomy- open stenotic valves Annuloplasty- can be used for both Valve Replacement Mechanical-need anticoagulant Biologic-only last about 15 years Ross Procedure Ross Procedure Nursing Diagnoses Decreased Cardiac Output Activity Intolerance Risk for Infection Ineffective Protection Case study http://edcenter.med.cornell.edu/Pathophysiology_Case s/96-97_Pathophysiology_Cases/96-97Case_04.html Cardiomyopathy Primary-idiopathic Secondary Ischemia infectious disease exposure to toxins Metabolic disorders Nutritional deficiencies Pathophysiology Dilated Most common Cocaine and alcohol abuse Chemotherapy pregnancy Hypertension Genetic * Heart chamber dilate and contraction is impaired and get dec. EF% *Dysrhythmias are common- SVT Afib and VT Prognosis poor-need transplant Pathophysiology Hypertrophic Genetic Also known as IHSS or HOCM Get hypertrophy of the ventricular mass and impairs ventricular filling and CO Symptoms develop during or after physical activity Sudden cardiac death may be first symptom Symptoms are dyspnea, angina and syncope Pathophysiology Restrictive Least common Rigid ventricular walls that impair filling Contraction and EF normal Prognosis-poor Diagnostics Echo-wall motion and EF EKG CXR Hemodynamics Perfusion scan Cardiac cath Myocardial biopsy Medications Same as for heart failure except for hypertrophic Treatment Surgery Vad-bridge to transplant Heart Transplant Myoloplasty ICD- antiarrhythmics are negative inotropes Dual chamber pacemaker Hypertrophic- excision of ventricular septum Heart transplant virtual transplant Nursing Diagnoses Decreased Cardiac Output Fatigue Ineffective Breathing Pattern Fear Ineffective Role Performance Anticipatory grieving Aortic Aneurysms Definition Abnormal dilation of a blood vessel at a site of weakness or a tear in the vessel wall. Usually secondary to atherosclerosis. Most commonly affect the aorta Layers of an artery AAA Aneurysms location Saccular Fusiform Most are fusiform and 98% are below the renal artery False or Pseudo A pseudoaneurysm is actually a disruption in the intima and media of the aorta, and only the adventitia/surrounding tissue retains blood within the aortic cavity. Ex. A hemotoma after a heart cath Dissecting Blood invades or dissects the layers of the vessel wall Aortic dissection occurs when blood enters the wall of aorta, separating its layers, and creating a blood filled cavity. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Frequently asymptomatic May have substernal, neck or back pain Other symptoms depend on location and structures they compress Abdominal Aortic Pulsating mass in mid and upper abdomen and bruit over the mass Pain intensity correlates to size and severity May have thrombi It can rupture causing shock and death in 50% of rupture cases Aortic dissection Life threatening emergency Happens when the intima tears and causes hemorrhage into the media Hypertension is main cause *Primary symptom is excruciating pain May get syncope,dyspnea and weakness Peripheral pulses are absent Diagnostic Tests for Aneuysms Most are diagnosed on routine work-up CXR Abd. Ultrasound TEE CT or MRI Angiography Medications Anti-hypertensives Beta blockers, Vasodilators Calcium channel blockers Nipride Sedatives Niacin, mevocor, statins Post-op anti-coagulants Surgery Usually repaired if >5cm Open procedure- abd incision, cross clamp aorta,aneuysm opened and plaque removed, then graft sutured in place Pre-op assess all peripheral pulses Post-op-check urine output and peripheral pulses hourly for 24 hours- (when to call Dr.) Endovascular stents- placed through femoral artery Nursing Assessment Pain- chest, abd or back pain Hypertension(other vital signs) Peripheral pulses Pulsation in upper abdomen SOB Nursing Diagnoses Risk for Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Risk for Injury Anxiety Pain Knowledge Deficit Prevention Prevent atherosclerosis Treat and control hypertension Diet- low cholesterol, low sodium and no stimulants Careful follow-up if less than 5cm. It can grow .5cm /year Complications Rupture Back pain Hypotension Pulsating mass Thrombi Renal Failure Rupture Triad Back pain Hypotension Pulsating hematoma http://www.cotc.edu/vstone/wk3.htm http://www.medi-smart.com/cardce5.htm