* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Pacemaker
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
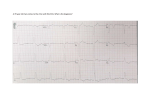
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
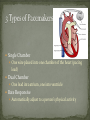
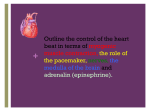
BME 181 March 4, 2013 Presented by: Corey Gomes J.A. McWilliams Late 1800’s Electrical impulses John Hopps Radio frequencies Mechanical and electrical methods External device Electrical signal spreads the length of heart Causes heart to contract and pump blood Starts in sinoatrial node Coordinates timing of heart cell activity Atria Pumps blood into the hearts two lower chambers Ventricles Pumps blood to rest of body Combination is the heartbeat Pacemaker has ability to create this electrical energy around the heart Small device that can take over the hearts electrical system Contains: Casing Nontoxic materials Titanium or titanium alloy Leads Thin insulated wires Metal alloy Carry electricity from battery to heart Circuitry Heart monitoring sensors Voltage regulators, timing and externally programmable controls Resistors, capacitors, diodes and semiconductors Battery Stores energy to stimulate heart and provides power to sensors 5 volts of power Predictable lifestyle Weighs about an ounce Implanted just below the collarbone 2 hour operation Single Chamber One wire placed into one chamber of the heart (pacing lead) Dual Chamber One lead into atrium, one into ventricle Rate Responsive Automatically adjust to a person’s physical activity Arrhythmias Problems with rate or rhythm of the heartbeat Bradycardia Heart beats too slowly Damage vital organs Atrial fibrillation Heart beats too quickly Heart failure Lack of blood and oxygen to brain Cons: Battery must be replaced Cannot be near EMI (electromagnetic interference) Must wait to perform strenuous activity Cautious with certain types of MRI machines Pros: Average life: 5-10 years Maintain regular lifestyle Monitor blood temperature and breathing rate Small & lightweight Two hour operation Low fail rate Battery life Main focus Radioactive isotopes for power Lighter and more efficient batteries Pacemaker technology to the brain Medtronic Device can detect problem and call an ambulance while the patient is asleep http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC15020 62/ http://www.medicinenet.com/pacemaker/page2.htm http://www.whoinventedit.net/who-invented-thepacemaker.html http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/healthtopics/topics/pace/ http://www.madehow.com/Volume-3/Pacemaker.html http://www.arrhythmia.org/pacemaker.html