* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy and Physiology - Killingly Public Schools
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
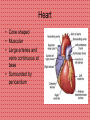
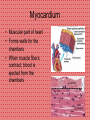
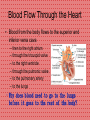
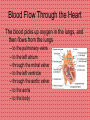
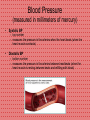
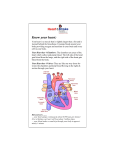
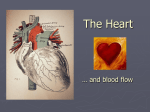
Anatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System Heart • Cone shaped • Muscular • Large arteries and veins continuous at base • Surrounded by pericardium Myocardium • Muscular part of heart • Forms walls for the chambers • When muscle fibers contract, blood is ejected from the chambers Heart Valves • Located between the atria and ventricles are called atrioventricular (A-V) valves • Valve on right = tricuspid valve (3 cusps) • Valve on left = bicuspid valves (2 cusps) • Prevent expulsion of ventricular blood into atria when ventricles contract Blood Flow Through the Heart • Blood from the body flows to the superior and inferior vena cava – – – – – – then to the right atrium through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle through the pulmonic valve to the pulmonary artery to the lungs •Why does blood need to go to the lungs before it goes to the rest of the body? Blood Flow Through the Heart The blood picks up oxygen in the lungs, and then flows from the lungs – to the pulmonary veins – to the left atrium – through the mitral valve – to the left ventricle – through the aortic valve – to the aorta – to the body Resting Heart Rates a a Species bpm (range) Cat 120–140 Chick 350–450 Chicken (adult) 250–300 Dairy cow 48–84 Dog 70–120 Elephant 25–35 Goat 70–80 Guinea Pig 200–300 Hamster 300–600 Horse 28–40 Mouse 450–750 Ox 36–60 Pig 70–120 Rabbit 180–350 Rat 250–400 Rhesus monkey (anesthetized) 160–330 Sheep 70–80 Adapted from Detweiler D.K. and Erickson H.H., Regulation of the Heart, in Dukes' Physiology of Domestic Animals, 12th ed., Reece W.O., Ed. Copyright 2004 by Cornell University Blood Pressure (measured in millimeters of mercury) • Systolic BP – top number – measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats (when the heart muscle contracts) • Diastolic BP – bottom number – measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats (when the heart muscle is resting between beats and refilling with blood) Characteristic Blood Pressures in Adult, Resting Animals Species Species Systolic/diastolic (mm Hg) Mean (mm Hg) Giraffe 260/160 219 Horse 130/95 115 Cow 140/95 120 Swine 140/80 110 Sheep 140/90 114 Human 120/70 100 Dog 120/70 100 Cat 140/90 110 Rabbit 120/80 100 Guinea pig 100/60 80 Rat 110/70 90 Mouse 111/80 100 Turkey 250/170 190 Chicken 175/145 160 Canary 220/150 185 Determines average rate at which blood flows through the vessels Detweiler D.K. and Erickson H.H., Regulation of the Heart, in Dukes' Physiology of Domestic Animals, 12th ed., Reece W.O., Ed. Copyright 2004 by Cornell University