* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1000 High Middle Ages
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Medieval music wikipedia , lookup
Islamic world contributions to Medieval Europe wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
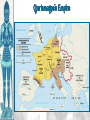
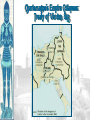
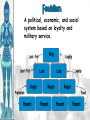
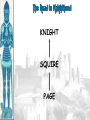
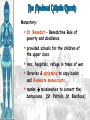
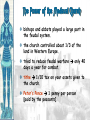
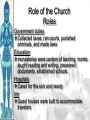
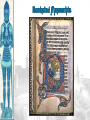
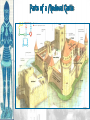
Background/Some images and some notes slidesare from the Ms. Pojer at historyteacher.net Rome Collapsed in 476 A.D Periods of the Middle Ages Early Middle Ages: 500 – 1000 High Middle Ages: 1000 – 1250 Late Middle Ages: 1250 - 1500 WHY WAS EUROPE A FRONTIER LAND IN THE EARLY MIDDLE AGES? • What is a frontier land? • Location. Europe is a relatively small area, although its impact on the modern world has been enormous. It lies on the western end of Eurasia. WHY WAS EUROPE A FRONTIER LAND IN THE EARLY MIDDLE AGES? • Resources. At the time of the Middle Ages, Europe had great-untapped potential. Dense farmland covered much of the North, and the region’s rich black earth was better suited for farming. WHY WAS EUROPE A FRONTIER LAND IN THE EARLY MIDDLE AGES? • The seas that surround much of Europe were important to its growth. A. Fishing B. Trade C. Exploration of new lands • Large rivers were ideal for trade. Mountain streams fueled the invention of the water wheel for powering mills. Paving the way for Charlemagne • Between A.D. 400 and 700, the Germanic tribes carved up Western Europe into small kingdoms. **The Franks were Powerful • **No real cities or written laws. People lived in small communities ruled by kings. • Frankish leader Clovis became Catholic. He now had the support of the Romans and church. • 480 Clovis became King of the Franks and conquered the province of Gaul. Paving the way for Charlemagne • Circa 800 Charlemagne built an empire reaching across France, Germany, and part of Italy. • The Pope proclaimed him emperor. • We now call this the Holy Roman Empire. He extended the Christian civilization into. • He also set up a strong government that was used as an example for medieval rulers. • After his death his empire crumbled. Pope Crowned Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor: Dec. 25, 800 Charlemagne: 742 to 814 Charlemagne’s Empire Charlemagne’s Empire Collapses: Treaty of Verdun, 843 HOW DID INVASIONS EFFECT THE PEOPLE OF WESTERN EUROPE? • Attacks by the Vikings, Muslims, and other groups of people, made kings and emperors too weak to maintain law and order. • People needed a way to defend their homes and lands. • In response to the basic need for protection, a new government started called Feudalism. Europe in the 6c Feudalism A political, economic, and social system based on loyalty and military service. The Medieval Manor Life on the Medieval Manor Serfs at work MANORIALISM • • • • • • The land the vassal received was called a manor (fief). It included a manor house, farmland, and a group of peasants. Most were serfs. Each manor was self-sufficient/self supporting. Raised most of what they needed to live. Grew their own food. Raised farm animals for food and wool. Managed trees for fuel and lumber. **Economic system of the Middle Ages** MANORIALISM • During the Early Middle Ages towns all but disappeared from Europe. Rome the Largest city of its time went from 1 million people to only a few thousand. • Around the 10th century, things began to improve and towns and trade began to grow. The Carolingian Renaissance The Rise of European Monarchies: England The Road to Knighthood KNIGHT SQUIRE PAGE The Road to Knighthood Role of a knight Most important member of the feudal army Main job was fighting Served his master Defended Christianity Chivalry: A Code of Honor and Behavior Chivalry-Honored set of rules sworn to by all knights. Emphasis upon courage, loyalty, devotion to duty, courtesy towards and defense of women, protected the poor, the weak the needy. Stages of Knighthood Stage #1 Page (age 7+) Learned to ride a horse Learned manners Had religious instruction (learned to read) Trained in music and dance by the ladies of castle. Stages of Knighthood Stage #2 Squire (age 12+) Assisted knights Became the lords devoted assistant Took care of armor and weapons and became skilled in their use. Helped in tournaments Stages of Knighthood Stage #3 Knight (age- when qualified) Knighted by the King Heraldry Heraldry is also called a coat of arms Used as identification on a knight’s shield during battle Heraldry What does it mean? The Medieval Catholic Church Monastery: St. Benedict – Benedictine Rule of poverty and obedience. provided schools for the children of the upper class. inns, hospitals, refuge in times of war. libraries & scriptoria to copy books and illuminate manuscripts. monks missionaries to convert the barbarians. [St. Patrick, St. Boniface] The Power of the Medieval Church bishops and abbots played a large part in the feudal system. the church controlled about 1/3 of the land in Western Europe. tried to reduce feudal warfare only 40 days a year for combat. tithe 1/10 tax on your assets given to the church. Peter’s Pence 1 penny per person [paid by the peasants]. Role of the Church Influence Spread Christianity Converted barbarians to Christianity Unified Europe Monks saved knowledge from past civilizations Introduced Roman ideals of government and justice Role of the Church Roles Government duties Collected taxes, ran courts, punished criminals, and made laws Education monasteries were centers of learning, monks taught reading and writing, preserved documents, established schools. Hospitals Cared for the sick and needy Inn Guest houses were built to accommodate travelers Corruption • • • • lack honesty, use of a position of trust for dishonest gain. involvement in feudalism led to corruption and the fall of the church. Awarded fiefs to wealthy church members. Bishops and monks took on the role of vassals. Loyalty of the church was divided between spiritual duties and economic duties. A Medieval Monk’s Day A Medieval Monastery: The Scriptorium Illuminated Manuscripts Romanesque Architectural Style Rounded Arches. Barrel vaults. Thick walls. Darker, simplistic interiors. Small windows, usually at the top of the wall. Carcassonne: A Medieval Castle Parts of a Medieval Castle Late Medieval Town Dwellings Medieval Trade Medieval Guilds Guild Hall Commercial Monopoly: Controlled membership apprentice journeyman master craftsman Controlled quality of the product [masterpiece]. Controlled prices Medieval Guilds: A Goldsmith’s Shop Crest of a Cooper’s Guild • Background/images/some note slides are from the historyteacher.net