* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Fall of Ancient Rome and the Rise of the Middle Ages
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 11th century wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
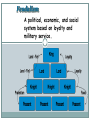
The Fall of Ancient Rome and the Rise of the Middle Ages Ancient Rome Polytheistic: Believe in many Gods Julius Caesar: First in a long line of Roman Emperors Octavian Augustus: Emperor as Rome enters the Pax Romana – a time of relative peace and unity Christianity Jesus Christ: Talks to everyone about the promise of eternal life to all if they love God, their neighbors and themselves Peter: The “rock” on which the Church will be built Paul: Messenger who preaches and spreads the beliefs of Jesus The Middle Ages Monotheistic: Believe in one God Germanic Tribes: Invade the Western Roman Empire and disrupt trade and weaken cities Charlemagne: Spreads Christianity through his conquests and builds an Empire that crumbles upon his death Pope Crowned Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor: Dec. 25, 800 The Medieval Catholic Church filled the power vacuum left from the collapse of the classical world. Monastery living (religious way of life for monks): Took a vow of poverty, chastity, and obedience. provided schools for the children of the upper class. inns, hospitals, refuge in times of war. libraries to copy books. monks missionaries to the barbarians. The Power of the Medieval Church the church controlled about 1/3 of the land in Western Europe. tried to curb feudal warfare only 40 days a year for combat. stop heresies crusades; Inquisition tithe 1/10 tax on your assets given to the church. Feudalism A form of government based on loyalty Designed to protect the king’s land Used throughout Europe, the Middle East and Japan Feudalism looks like a pyramid Feudalism A political, economic, and social system based on loyalty and military service. Carcassonne: A Medieval Castle Parts of a Medieval Castle Life on the Medieval Manor Serfs at work The Power of the Church The Roman Catholic Church taught people to accept their place in the feudal pyramid The Church taught that it was the soul that mattered so hardships faced during life would lead believers to eternal life in heaven Add to the top of your illustrated timeline The following events contribute to the regression of Western Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire. Your timeline should have an image and a one or two sentence summary that explains the event. Be sure to use color on your timeline. 476 - The Fall of the Western Roman Empire 600 - The Christian Began to Dominate Religious & Political Life (p. 370-373) 911 - Development of Feudalism (p. 360-363) 1095 - 1291 Crusades (p. 382-385) 1347- Bubonic Plague (p. 399-401)