* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam & the Crusades - RoshanVarghese
Regensburg lecture wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Europe wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
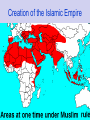
WarmUp #5 • Analyze the map on pg. 256: “Starting Points: Arabia ~550 A.D.” • Answer the “Analyze & Predict” questions. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Objective: Analyze the rise & spread of Islam & its influence on the Crusades, as well as Christianity in the Late Middle Ages. Arab World • nomadic people • polytheistic – believed Abraham built kaaba at Mecca • believed in supreme god called Allah Mohammed 570-632 AD • orphaned, caravan leader (wealthy) • troubled by gap between rich & poor • meditated: visions of the angel, Gabriel – recorded = Koran (Quran) • preached in Mecca – people chased him out, so he fled to Medina 622 AD (hijrah) • converted people in Medina – returned to Mecca with an army & conquered city 630 AD Muslim Teachings • monotheistic: Allah • holy book: Quran • must follow the 5 Pillars of Islam – belief: “there is no god but Allah & Mohammed is His messenger…” – prayer: 5 times a day, facing holy city of Mecca – alms/charity: give to the poor/less fortunate – fasting: dawn to dusk during the holy month of Ramadan – hajj: pilgrimage to Mecca once in life, if able (health/$$$) • salvation, by following will of Allah Muslim Teachings • Shariah: strict Islamic law code • Sunna: Muhammad’s behavior/teachings – Muslims are not allowed to gamble, drink alcohol, eat pork, be dishonest etc Culture of Islam • Mohammed: last/greatest prophet • mosques: places of Muslim worship • trade: main activity – Islam spread through conquest & trade • initially, women had some rights (~Mohammed’s wife) – over time, they have lost rights • patriarchal: men could have up to 4 wives Art, Literature & Architecture • Quran seen as greatest literature • architecture is best seen in mosques: Muslim houses of worship – minarets (towers on mosques: calls people to pray) • not allowed to make human images…so repeated geometric patterns to form arabesques • palaces: constructed with huge fortifications – borrowed by Europeans for castles Mosque Art & Architecture Preservation of Knowledge • preserved numerical system from Ancient India • created algebra & navigational tools • separated the study of medicine from the other sciences • Ibn-Khaldun: historian, who saw history as being cyclical (always repeats itself) After Mohammed’s Death • no clear successor • Abu Bakr became caliph – Islamic leader/Mohammed’s successor • took over Arabian Peninsula (jihad) – conquered Syria, Egypt, old Persian Empire • Abu Bakr’s death: series of caliphs Spread of Islam Umayyad Dynasty: 661-750 AD Umayyad Dynasty • moved capital to Damascus, Syria • marched across N. Africa & into Europe – – – – 700 AD: conquered Berbers 710 AD: crossed Gibraltar into Spain 725 AD: controlled Spain w/ capital at Cordoba 732 AD: defeated by Charles Martel at the Battle of Tours (France) • built the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem (on the Temple Mount: site of Solomon’s Temple) • people felt Umayyads showed excessive favoritism – led to downfall of dynasty Battle of Tours Creation of the Islamic Empire Islamic World Split in Islam • Hussein led revolt against Umayyad rulers – outnumbered & defeated but led to split in Islam – Shiite Muslims • only descendents of Ali: true leaders of Islam (imams) • mostly in Iran & Iraq – Sunni Muslims: • believe leader should be chosen by council • majority of Muslims worldwide Seljuk Turks • conquered eastern Arab world by the 11th Century • 1055 AD: took over Baghdad & proclaimed their ruler, the sultan: holder of power • 1071 AD: defeated the Byzantines to take over Asia Minor prophet deity belief in 1 god the 5 Pillars Areas where Islam has spread? ISLAM holy book followers Islam & the Early Arab World Directions: Fill in the following boxes using your textbook. Sunni beliefs: Shiite/Shia beliefs: Islamic Beliefs/Practices Umayyad Dynasty Contact with Christians/Europeans Islamic Achievements Islam & the early Arab World Directions: Put the following terms/people/events in the correct box. Islamic Beliefs/Practices Umayyad Dynasty •following the 5 Pillars of Islam •not drinking •polygamous: having up to 4 wives •women = modest •read the Quran in Arabic •expanded Islam across Northern Africa & into Europe Contact with Christians/Europeans Islamic Achievements •invasion of Constantinople •Crusades in Middle East (Jerusalem) •invasion/occupation of Spain •Battle of Tours (France) •numerical system of Ancient India •medical knowledge •algebra •navigational tools (astrolabe) The Crusades Crusades: 11th-13th Centuries • military expeditions: European Christians (Roman Catholics) trying to recapture Jerusalem in the Holy Land from the Muslims • Pope Urban II: saw the Byzantine request for help as his excuse to take power – preached importance of the 1st Crusade: 1095 AD • most warriors were French…religious zeal, but also wanted wealth, glory, power, bloodlust etc. • 1st Crusade: 1095-1099 AD…bloody fighting, but the Christians conquer Jerusalem & Antioch • set up 4 Crusader kingdoms, creating great trade opportunity for Venice, Genoa, etc. • 2nd Crusade: Muslims rebuilt power, attacked & retook all the land, Christians won in the 1st Crusade 3rd Crusade (~1189 AD) • European Leaders: – Frederick Barbarossa (Holy Roman Empire) – Richard I (England) – Phillip II (France) • big problems: – Frederick Barbarossa drowned – Phillip II returned to France – Richard I negotiated peace • Saladin: Muslim leader…great warrior, who was very merciful – Richard I & Saladin had great respect for one another 3rd Crusade: Acre Crusades (ctnd.) • 4th Crusade: Pope Innocent III calls for another crusade, with serious backing of Venetian merchants • instead of helping the Byzantium Empire, the Crusaders sack Constantinople • Byzantines regained control of city: 1261 AD • Children’s Crusade to Rome…sent home • Effects of Crusades: – kings took land from knights who did not return – greater trading power to Venice & other Italian city-states – widespread persecution of Jews in Europe (antiSemitism) – extensive knowledge of Muslim culture in Europe In-Class Assessment 1. Who is the founder of Islam & what city is he from? 2. List the 5 Pillars of Islam. 3. Muslim houses of worship are called _______ & the towers attached are called __________. 4. What were the Crusades? 5. Why were the Crusades controversial when analyzing them from the Christian viewpoint?