* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam - Yola
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
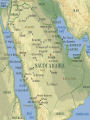
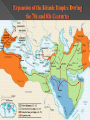
The spread of major world religions across political and cultural borders and the development of a new, more regular system of trade that connected much of Asia, Africa, and Europe. The spread of trade helped disseminate religion, and confidence in a divine order helped merchants take risks. A trigger for this change was the economic decline and disorder associated with the decline of the classical empires. Religion and commerce were the engines of change in the postclassical period. Both facilitated the spread of technologies, ideas, and disease. Even though the classical empires collapsed, the successes of classical civilization encouraged many people to maintain or revive classical forms. The impact of this time period on the daily life of women was noticeable. The postclassical period saw an intriguing tension on the roles of women as religions insisted on equality but societies clung onto the patriarchal culture. Islam first appeared on the Arabian Peninsula › Bedouin pastoral nomad tribes Goat and Camels Some small agricultural settlements south › Towns like Mecca developed along coasts Clan Loyalty and rivalry › Clans had different Clan Idols Blend of animism and polytheism Art was largely nonexistent (maybe the Idols) Shaykhs were leaders of the Bedouin Women enjoyed somewhat greater freedoms Then something changed…. Arabia and Surrounding Area Before and During the Time of Muhammad (Born 570 Mecca – Died 632 Medina) Founder of the religion of Islam regarded by Muslims as a messenger and prophet of Allah after receiving a message from archangel Jobril “Gabriel” (610 CE) › The last and the greatest law-bearer in a series of 28 Islamic prophets › Restorer of the uncorrupted original monotheistic faith of Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, Jesus and other prophets Also a diplomat, merchant, philosopher, orator, legislator, reformer, & military general The start of political empires and major culture change Mohammad unified the Arab tribes under religion, but would also become a political system: So, after Mohammad’s Death…Ridda Wars happened to restore unity of the tribes (faith) Political structures: › Mohammad’s father-in-law Abu Bakr assumed leadership of the Umma (the faithful, followers of prophet) › Ali (Mohammad’s son-in-law & blood descendant) was passed over. The catalyst of the Sunni-Shi’s split Form of Government- Theocracy Empires › Umayyad Caliphate(661-750) capital in Damascus, captured Mesopotamia, N. Africa, & Persia › Abbasid Caliphate(750-1258) moved the capital to Bagdad. The first 300 years are known as the zenith of Islamic civilization as a single religious and political entity Revolts and Revolutions- › Hijra- 622 CE (Islam year one) Mohammad & his followers forced out of Mecca and fled to Medina (200 miles/320kilometres) 622-630 marked with battles with other Arabian tribes Mohammad returned to Mecca with 10k men Regional, trans-regional, and global structures & organizations Conflicts or Revolts › The Sunni & Shiite split- 656-661 disputes in Mohammad’s family led to civil war – when Caliph Ali was assassinated in 661, Shiites believed the Umayyads to be usurpers › This conflict still remains today… › Umayyad’s extravagance led to the empire’s overthrow in 750 › Crusades (1095 – 1291) more detail during Europe Agricultural & pastoral production › Conquered areas had crops Arabs never seen before: sugar cane, rice, spinach, artichokes › Shared new crops & farming techniques › Increased food supply = surplus crops growth of cities Trade & Commerce › Merchants & Landlords grew in wealth & status. › A boat called ‘dhow’ improved sailing, carried goods across Indian Ocean & Mediterranean Sea Routes Labor Systems › Slave labor became increasingly important for unskilled work › Craftsman- catering to the wealthy: furniture, carpets, glassware, jewelry, & tapestries Industrialization › All the above stimulated new businesses › Cities like Baghdad, Damascus, Jerusalem, and Cairo grew Religion(s)- The word Islam comes from the Arabic phrase “to submit to God” Universal & ethnic religion that has diffused around the world Sacred Place(s) Ka’ba in Mecca, Medina, Dome on the Rock, Masque in Istanbul Important texts: Quran (Koran), Belief systems: Abraham is the patriarch His son Ismail (Ishmeal) is their direct ancestor Other major prophets: Adam, Noah, Moses, David, Solomon, John the Baptist & Jesus › Muhammad believed he was the last of 28 prophets › › › › › › Muslims respect Jews & Christians as “people of the book” Term Muslim in Arabic means –”one who has submitted to the will of God” Philosophies Five Pillars of Islam- the fundamental obligations of Islam that distinguish it from Christianity and Judaism › 1. Testimony of faith, 2. Prayer (Daily Worship 5 times a day), 3. Almsgiving (Annual Tax) 4. Fasting (Ramadan), 5. Pilgrimage (Mecca 1x in life) › Ideologies Sufism- appeared 700-800CE a mystical tradition of fasting, prayer, & meditation to grow closer to Allah (Prominent in Iran) › Jihad› Science- Built on the mathematical knowledge of ancient Hindu scholars › Algebra › Arabic numerals still used today › Optical science, pharmacology, & anatomy Key Technology- › Borrowed inventions from China: Paper, Compass, gunpowder, Arts- › Distinct from most others because of its intricate, geometrically based format Quran strictly forbade the lifelike representation of human figures esp. of Muhammad or Allah Architecture- Art carried over to public buildings, colored ceramic tiles, › Domes, Arches, Columns, Minaret(Prayer Tower) Gender roles and relations › Women- Dress restrictions, appearance in public, modesty, veil Right to inherit, have dowries, and own property › Men – Male domination was offset by the command to treat women with respect Family and kinship › Polygamy up to 4 wives (Concubines, Harem) Racial and ethnic constructions › Abbasids fully integrated the ‘Mawali’ into the Islamic community Social and economic classes › Ayans – Land owning Elite. Dhimmis- people of the book were protected (Jews, Christians, & Zoroastrianism) Slaves important as Bedouin settled down. Language- Arabic was a unifying force in the Islamic caliphates= Quran only written in Arabic Writing systems- Arabic, paper made sharing of ideas & writing books much cheaper › Many books “Golden Age” (Poetry sung aloud in Arabic-Jalal al-Din al-Rumi) › Many love stories & folktales = “The Thousand and One Nights” Learning- Madrasas (Universities) Scholars sought to preserve works of the Greek, Roman, and Indian civilizations Demography = Population Increase Migration- of Arabs via the different Islamic Empires Crusades by Europeans migrating to Islamic areas between1095 and 1291 not much cultural change. Patterns of settlement- Nomads became urban Technology’s impact on environment Dar-Islam developed into one of the most dominant influences throughout the eastern hemisphere (Eurasia, Africa) › Even through Mongol invasions Dar-Islam thrived. Dar-Islam - Muslims culture and life styles Patriarchy Nomadic conflict with settled, advanced, urban cultures Major cities centers of trade and culture Changing Empires: › Umayyad 661-750 (Internal Riots by general public because of › Abbasids 750-1258 (Mongols sack Baghdad) › Mamluk Dynasty- Mongols who made Egypt the center of Islam culture (sacked by Ottomans later 16th century) › After Mongols, new empires of Ottomans (Turkey), Safavids (Persia), Mughals (Delhi Sultanate, India) Started in 1300s-1400s Increase of long distance trade, interactions of Indian Ocean & TransSaharan trade routes creating new trade Analyze gender systems & changes Interactions between Jews, Christians, & Muslims Compare European & sub-Saharan African contacts with Islamic World