* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Day 4 - Ch.5(21)Cycles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
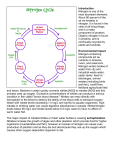
Chapter 5 Ecosystems and the Physical Environment The Gaia Theory Dynamic Equilibrium Negative Feedback Positive Feedback The Gaia Theory: The organic and inorganic components of Planet Earth have evolved together as a single living, self-regulating system. In a phrase, “life maintains conditions suitable for its own survival.” How Chemicals Cycle Biogeochemical Cycle The complete path a chemical takes through the four major components – or reservoirs – of Earth’s systems 1. 2. 3. 4. Atmosphere Hydrosphere Lithosphere Biosphere Cycles Carbon 1. Lipids 2. Nucleic Acids 3. Carbohydrates 4. Amino Acids Nitrogen 1. Amino Acids Phosphorus 1. ATP 2. DNA 3. Cell Membranes Sulfur 1. Amino Acids 2. Keratin Fixed amounts of all elements on earth * Oxidation describes the loss of electrons by a molecule, atom or ion * Reduction describes the gain of electrons by a molecule, atom or ion Carbon Cycle Billions of Tons http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= 0Vwa6qtEih8&feature=related Carbon Silicate A weathering Cycle: 1.Atmospheric CO2 forms H2CO3 (Carbonic Acid) precipitation which moves through soil 2.H2CO3 dissociates & forms H+ & HCO -3 (bicarbonate) 3.Silicate rich minerals interact with the free H+ to release Ca2+ 4.Shellfish 5.Subduction – silicate formation at temperatures above 300 °C Carbon Silicate Believed to provide important negative feedback mechanisms that control the temperature of the atmosphere. Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen cycle: Biological nitrogen 1. fixation Lightning Volcanoes Bacteria (Ammonia) NH3 & NH4- Atmospheric nitrogen (N2) Nitrogen fixation by humans Decomposition - urea 5.Denitrification 4. Ammonification Plant & animal proteins Internal cycling 3. Assimilation (Oxidation) 2. Nitrification NO3- (Nitrates & Nitrites) Nitrogen Cycle & Steps 1. Nitrogen Fixation is the conversion of elemental nitrogen(N2) to organic ammonia(NH3) by bacteria, lightning, industry, volcanoes. 2. Nitrification - conversion of ammonia or ammonium (NH4) into nitrites(NO-2) and then into nitrates (NO-3) 3. Assimilation- plants absorb nitrates or ammonia 4. Ammonification - nitrogen is converted into ammonia from animal waste or dead organisms by aerobic bacteria 5. Denitrification - anaerobic bacteria convert nitrates & nitrites to nitrogen gasses off to atmosphere 1. Nitrogen is not a reactive molecule 2. 78% atmosphere N2 & 21% oxygen & .038% CO2 YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m4YToXw724w&feature=related Phosphorus Cycle Does not include the atmosphere YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RKkC2JpjaGc&feature=related Phosphorus Cycle Phosphorus Brazil Guano Accelerated Eutrophication Cycling of Materials within Ecosystems Sulfur cycle: YouTube: http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=BzPeA9oQ Nl8 Cycling of Materials within Ecosystems Hydrologic cycle: Tectonic Cycle Tectonic cycle: Involves creation and destruction of the solid outer layer of Earth, the lithosphere Plate tectonics: The slow movement of these large segments of Earth’s outermost rock shell (7 plates) Boundaries between plates are geologically active areas Internal Planetary Processes Volcanic Activity 2011 Internal Planetary Processes Plate boundaries Internal Planetary Processes Plate boundaries Tectonic Cycle: Plate Boundaries Divergent plate boundary: Occurs at a spreading ocean ridge, where plates are moving away from one another New lithosphere is produced (seafloor spreading) Convergent plate boundary Occurs when plates collide Produces linear coastal mountain ranges or continental mountain ranges Transform fault boundary Occurs where one plate slides past another San Andreas Fault in California Internal Planetary Processes Volcanoes Most volcanoes occur along subduction zones Internal Planetary Processes Volcanoes Some occur along spreading zones Few, such as Hawaiian Islands, not associated with plates. Internal Planetary Processes Earthquakes • caused by release of built up stress, typically along faults • movement releases seismic waves Typical side effects include: 1) Landslides 2) Tsunamis