* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapters 1 and 2 Review
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
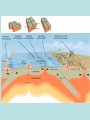
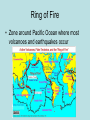
Chapters 1 and 2 Geography • Study of the distribution and interaction of physical and human features on the earth 5 Themes-Location • “Where is it?” • Absolute-exact • Relative-comparative 5 Themes-Place • “What is it like?” • Physical-landforms, climate • Cultural-religion, traditions 5 Themes-Region • “How are places similar?” • DFW • North Texas 5 Themes- Human-Environment Interaction • “How do people interact with the environment?” • Depend-rivers • Modify-roads • Adapt-clothes 5 Themes- Movement • “How do people, goods, and ideas move from place to place?” • Technology is most important Equator • An imaginary line that divides the earth into northern and southern halves Prime meridian • Imaginary line dividing the earth into eastern and western halves Hemisphere • Half of the earth • Northern, southern, eastern, western Globe • 3-Dimensional representation of earth • Not portable Cartographer • Person who makes maps • Map is 2-D, distorts landmasses, and is portable Topographic Map • Shows natural and man-made features on the earth Thematic Map • Emphasizes specific information like climate or vegetation or population GIS-Geographic Information System • A system that uses digital map information to create a databank • Can add or remove different layers to highlight certain information • • • • Economic – financial issues, business Social – Culture, society Political – government, leaders Nature – Environment, resources, physical geography Chapter 2 • Objective: Explain the physical forces that shape the Earth and how they affect people Hydrosphere • Includes all water on earth • Ocean=71% • The Blue Planet Lithosphere • The solid rockportion of the earth’s surface • Includes crust and upper most mantle Atmosphere • The oxygen we breathe, protects earth from radiation, allows for weather and climate to occur Hydrologic Cycle • Continuous circulation of water between earth, atmosphere and oceans Magma/Lava • Molten Rock under/above surface Tectonic Plates • Giant moving pieces of the earth’s crust Plate Movement • Divergent-move apart, spreading horizontally • Convergent-collide, one goes under or both crumple • Transform-slide past one another Ring of Fire • Zone around Pacific Ocean where most volcanoes and earthquakes occur Earthquake • Violent movement of the earth’s crust Volcano • Crack in the earth’s crust where molten rock exits • Often on a mountain or bulge • Violent Tsunami • Giant wave usually caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanoes Destruction during Japanese Tsunami 2011 Aftermath at vehicle shipping yard Weathering • Process which acts upon the earth's surface to decompose and breakdown rocks and earth. Glacier • Large, slow moving mass of ice. Moves because of gravity Erosion • The movement of weathered material by wind, water, or ice