* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Restless Continents
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
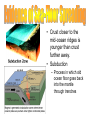
• Theory that all of the continents were once one large landmass (Pangaea) that has broken up and drifted apart. – Alfred Wegener • Evidence – Continents fit like pieces of a puzzle – Fossils of same species animal & plants found on separate continents • Glossopteris – Rock formations • Matching mountain chains – Climatic conditions • Coal fields in Antarctica • Pangaea – Greek for “ all Earth” • Pangaea broke into two huge continents – Laurasia – Gondwana • These two split again to form the current continents • Mid-ocean Ridges – Underwater mountain chain that runs through the Earth’s oceans. • Sea-floor spreading – Process in which new lithosphere forms • Magma rises to the surface through the mid-ocean ridge forming new oceanic crust • Tectonic plates spread apart and magma fills the gap. • As new crust forms older crust moves away from the M.O.R. • Crust closer to the mid-ocean ridges is younger than crust further away. • Subduction – Process in which old ocean floor goes back into the mantle through trenches • Earth’s north and south poles have changed places many times • Molten rock contains contains tiny grains of magnetic minerals • These minerals align with the magnetic field of the Earth. • As the magnetic field reverses and the ocean and new ocean floor is formed it leaves a record of this change.