* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ch 13 PPT File
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
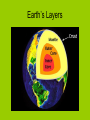
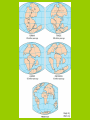
EARTH SCIENCE Movement of the Earth’s Crust The Earth’s Layers • The Earth is made up of three layers: • At the center is the core. The core is solid iron and nickel. The core is about 3,500 kilometers thick. • Outside the core is the mantle. Made of liquid and solid rocks that churn. The entire mantle is about 2,900 kilometers thick. • The outermost layer is the crust. Very thin and cold, 8-70 kilometers thick. The continents and oceans floor are part of the crust. Earth’s Layers Continental Drift • According to this theory, the Earth’s continents used to be joined as a single large landmass called Pangaea. Evidence of Pangaea • Besides the puzzle fit of the continents: 1. Fossils found on one continent were similar to fossils found on another continent. 2. Mountain layers seem to continue from one continent to another. 3. Glacier deposits were found at the equator where glaciers can not exist. Sea Floor Spreading • This theory states that hot magma from the mantle rises and pours out onto the ocean floor through cracks in a rift. The magma hardens cools and forms new crust. • This process continues, stretching the ocean floor and pushes the continents apart. • Atlantic Ocean grows 2 ½ inches per year. Plate Tectonics • This theory states that the Earth’s crust is made of large sections, or plates. Plate Tectonics • 1. 2. 3. • Plates move in three different ways: Move apart Collide Slide into each other These actions cause Earthquakes and volcanoes.