* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EARTHQUAKES
Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant wikipedia , lookup
2009–18 Oklahoma earthquake swarms wikipedia , lookup
Casualties of the 2010 Haiti earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Seismic retrofit wikipedia , lookup
2010 Canterbury earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1908 Messina earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2008 Sichuan earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
April 2015 Nepal earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1570 Ferrara earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1880 Luzon earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
2010 Pichilemu earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1992 Cape Mendocino earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
1906 San Francisco earthquake wikipedia , lookup
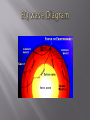
Section 21.2 WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE? An earthquake is a movement of Earth’s crust caused by a release of energy WHAT CAUSES AN EARTHQUAKE? Eruption of a volcano Collapse of a cavern or building Major cause – stress between two plates Friction builds up between two plates The stress causes the plates to deform or ‘stretch’ Eventually, the stress becomes great enough that it overcomes friction and the plates move The plates ‘snap’ back into their original shape and begin building up friction again Point on the fault (or plates) where movement first occurs Where an earthquake starts 3 types Shallow (0-70km) Intermediate (71-300km) Deep (301km and higher) Point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus What is reported as the location of an earthquake P-waves: primary waves; travel through solids, liquids, and gases; back and forth motion P waves are ______________ waves. S-waves: secondary waves; travel through solids only; side to side motion (snake) S waves are ___________ waves L-waves: surface waves Combination of up and down and back and forth motion Cause the most damage due to their rolling action and long wavelengths Seismograph: an instrument that detects and records earthquake waves P-waves always arrive first, then S-waves, then L-waves P and S Waves Graph – pg.767 – Under Graphing Skills As distance increases, the travel time for seismic waves increases also. To locate the exact location of an epicenter, you must have points from three separate seismograph locations around the world Richter Scale Developed by Charles Richter in the 1940’s Measures the amount of energy released by the earthquake itself Scale from 1-10 (weakest - strongest) Each number is 32 times stronger than the next lower number (Ex: ‘6’ is 32 times stronger than a ‘5’ and 1024 times stronger than a ‘4’) We cannot predict earthquakes other than giving periods of time in which we think they will occur. Earthquakes are most common along sliding plate boundaries, but they can occur in other places. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/learn/kids/