* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World Geography 2007 Chapter 2 Notes
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
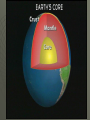
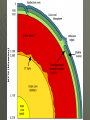
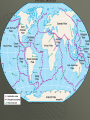
World Geography Chapter 2 Notes Looking at the Earth Section 1 Planet Earth The Solar System Earth is part of a solar system Sun is at center of solar system 1. Sun is a star 9 planets in the solar system 1. Earth is the 5th largest 2. Jupiter is the largest Earth’s measurements 93 million miles from Sun 3rd planet from Sun Water, Land , and Air 70% water 1. Hydrosphere – oceans, lakes, rivers Land 1. Lithosphere – Continents and ocean basins (land beneath oceans) Air 1. Atmosphere – extends approximately 1,000 feet above Earth’s surface Biosphere – part of Earth where life is found Earth’s heights and depths Mt. Everest – highest point ( 29,028 ft.) Mariana Trench – lowest point (35,000 ft) Average height above sea level – 2,800 ft. Inside the Earth (composed of four layers) Inner core – center of the Earth (4,000 miles. below the surface) Outer core – made of iron and nickel (begins about 1800 miles below the surface) Mantle – a thick layer of dense hot rock Crust – a thin layer next to the surface (3 to 30 miles deep) 1. continents and ocean basins Earth’s changing structure Constantly changing due to internal and external forces Internal Forces Forces cause plates to move Plate spread apart – forms a ridge Plates bump together – forms a trench Internal forces build and break down mountains Folds – bends in layers of rock Plates squeeze Earth’s surface until it buckles Faults – breaks in the Earth’s surface occurs when surface can’t be bent any further Internal Forces Continued Earthquakes and Volcanoes Can cause as much damage under the ocean as ones on land tsunami – giant tidal waves Often occur where plates meet Many occur along the edge of plates under the Pacific ocean 1. Called the Ring of Fire Continental Drift theory – geologist believe that all the continents used to be joined together (Pangea) External Forces Weathering – process that breaks down rocks 1.Chemical – water dissolves some of the chemicals in rocks. Causes them break apart 2. Physical – water seeps into the rocks freezes expands and causes the rocks to break apart External Forces Continued Erosion – wearing away of the Earth’s surface 1. Wind – movement of dust, sand, and soil from one place to another 2. Water – runoff digs into ground and rocks forms valleys and gullies Glaciers – destroy forest and land as they move across land Section 2 Earth’s Features Landforms Natural features of the Earth’s surface Classified by type to help people locate them Continents 7 large landmasses 1. Asia – largest 2. Australia – smallest Some people consider Europe and Asia to be one continent (Eurasia) 1. divided by the Ural Mountains Major landforms Mountains – highest landform, steep slopes with a peak or summit Hills - lower than mountains, more rounded Plateaus – higher than surrounding land, usually has one steep side (table top) Plains – flat or gently rolling lands 1. Coastal plains have lower elevations 2. Interior plains have higher elevations Peninsula – piece of land surrounded by water on 3 sides (Florida) Archipelago – a group or chain of islands (Hawaii) Continental Shelf – underwater extension of a continent Mountains highest landform, steep slopes with a peak or summit Hills lower than mountains, more rounded Plateaus higher than surrounding land, usually has one steep side (table top) Plains Flat or gently rolling lands 1. Coastal plains have lower elevations 2. Interior plains have higher elevations Peninsula Piece of land surrounded by water on 3 sides (Florida) Archipelago A group or chain of islands (Hawaii) Valley Water Saltwater Most of the Earth’s water is salty. Oceans 1. Pacific 2. Atlantic 3. Indian 4. Arctic Seas – bodies of salt water smaller than oceans Water Continued Freshwater Lake – body of water surrounded by land Stream – body of water flowing through land 1. Combine to form rivers 2. Rivers combine to form major waterways Groundwater – freshwater that lies beneath the surface 1. main source comes from rain and melted snow 3% of world’s water is fresh 2% trapped in glaciers .5% is groundwater .5% rivers and lakes Glaciers Water Continued Water cycle – regular movement of water from ocean to air to ground back to ocean 1. Begins with evaporation – changing of liquid water to gas Section 3 Earth’s Resources Natural resources Elements from the Earth not made by people but used by people 1. oil, water, soil Minerals – things from the earth that are not living or made from living things Fossil Fuels – formed from the remains of plants and animals 1. coal, oil, gas Value of resources Use, supply, and changes over time determine how valuable certain natural resources are 1. Gold 2. Rubber trees 3. Uranium Managing resources Renewable resources – can replace themselves 1. plants and animals Nonrenewable – can’t be replaced 1. iron and fossil fuels Recycle – to reuse but can’t replace Protecting 1. crop rotation 2. conservation Distribution of resources Not distributed evenly Influences how countries relate to each other Scarcity has lead to trade 1. Japan – imports raw material sells finished products Imports – what a country brings in Exports – what a country sends out