* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s interior volc eq1
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
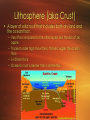
How the Layers Formed • As earth formed, it was made of hot molten magma and intense gravity. • As rocks melted, denser materials sank to the center of the Earth and became the core. • Less dense material rose to the surface and became the crust • The middle layer is the mantle. – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H6OuD877Rog • (formation of the Earth, 10 min) Lithosphere (aka Crust) • A layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and the ocean floor. – Very thin compared to the other layers, like the skin of an apple. – Thickest under high mountains, thinnest under the ocean floor. – 5-100 km thick – Oceanic crust is denser than continental. The Mantle • Made of very hot rock. – Mixture of solid AND liquid! So cool. – Asthenosphere: Upper mantle •Spelling - As The No Sphere •Moves tectonic plates – Mesosphere: lower mantle that extends to the core. The Core • Outer core: – molten (liquid) metal. – Movements in this part of the core causes Earth’s magnetic field. • Inner core: – dense ball of solid metal. • Both are made of iron and nickel, but the extreme pressure in the inner core keeps the metal a solid Earth’s Interior The composition and properties of Earth’s interior are identified by the behavior of seismic (earthquake) waves. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_mcC8kFacrk (formation of the earth video, 5 min)