* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter Two Notes
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
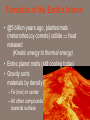
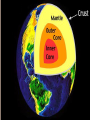
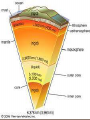
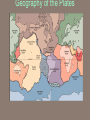
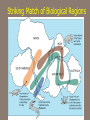
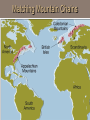
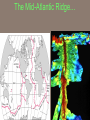
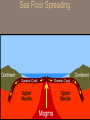
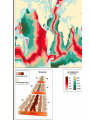
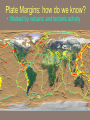
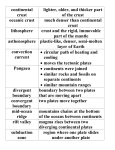
Chapter 2: Canada’s Physical Landscape Formation of the Earth 2.1 Formation of the Earth 2.1 Planet Earth Formation of the Earth’s Interior • @5 billion years ago, plantesimals (meterorites,icy comets) collide heat released (Kinetic energy to thermal energy) • Entire planet melts (still cooling today) • Gravity sorts materials by density – Fe (iron) in center – All other compounds towards surface Earth’s Four Layers • • • • Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core Scrat! The Crust • Outer layer • 5-100 km thick • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense) – Continental (less dense) The Mantle • Middle layer • Very thick layer The Core • Made mostly of iron • 1/3 of the earth’s mass • Very hot Earth’s Layers • How are the earth’s layers similar to an egg? • Shell=crust • Egg white=mantle • Yolk=core The Earth’s Interior Distance: 6730 km (3963 miles) What is ‘ Plate Tectonics’? • From Greek ‘tektonikus’ meaning building or construction • Plate tectonics refers to the process of plate formation, movement, and destruction. How the Plates Moved…. Tectonic Plates • Earth’s crust is broken into about 19 pieces • These plates move on top of the crust. Geography of the Plates • 1915 Alfred Wegener proposes theory of continental drift. • Supercontinent Pangaea (‘all-earth’) [225mya]. • Continents ‘broke apart’ and moved into current positions. Plate Movement History Evidence for Continental Drift? • Wegner’s evidence – Fit of continents – Match of magnetic bands on rocks on either side of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge – Fossil plants, animals, rock types / geology • match on opposite shores • deposits inconsistent with current geography Glacial deposits, including structures that indicate ice flow direction are located in ancient rocks as shown on the left. Wegener suggested that the pattern formed with continents together at the south pole. Striking Match of Biological Regions The Theory of Continental Drift Matching Mountain Chains Striking Match of Geologic Regions The Mid-Atlantic Ridge… Mid-Atlantic Ridge ‘In Action’! Sea Floor Spreading Bill Nye Plate Margins: how do we know? • Marked by volcanic and tectonic activity • Crustal Processes – Destruction (subduction) – Creation (volcanism) – Alteration / deformation (folding and faulting) Subduction Zone? Subduction Zones • Activity: – Subduction zone; shallow to deep earthquakes; volcanism (continental) • Examples: – ocean trench (Pacific Ocean by Japan); explosive volcanic mountains ‘Ring of Fire’ Subduction Zones How Might the Continents Look in the Future?