* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
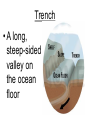
Pangaea • The name of the single landmass or supercontinent Continental Drift • The movement of continents as described by the theory of plate tectonics. Plasticity • capacity for being molded or altered Plate Tectonics • A theory that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle Rift Valley • A deep valley that forms where two plates move apart. Mid-Ocean Ridge • The undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary Trench • A long, steep-sided valley on the ocean floor Subduction • oceanic crust sinks beneath another plate and back into the mantle; convergent boundary Sea/Ocean Floor Spreading • The building of new ocean floor at a divergent plate boundary Volcano • An opening in the earth's crust through which molten lava, ash, and gases are ejected Earthquake • A sudden movement of the earth's crust caused by the release of stress accumulated along geologic faults or by volcanic activity Fault • a break or crack in the crust where the rocks can move Weathering • to expose to the action of the elements Erosion • the process by which the surface of the earth is worn away by the action of water, glaciers, winds, waves, etc. Topographic Map • a map showing topographic features, usually by means of contour lines.