* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint - Vernon Hills High School
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Polar ecology wikipedia , lookup
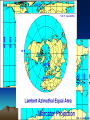
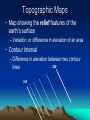
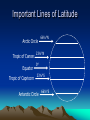
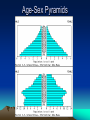
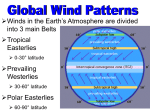
5 Themes of Geography a. What is it like? b. Where is it? c. How do people relate to the physical world? d. How do people, goods, & ideas move from one place to another? e. How are places similar or different a. Place b. Location c. Human/Environment Interaction d. Movement e. Region Latitude & Longitude Hemispheres 90 º North (º North, º West) (º North, º East) Equator West 180 º East 180 º (º South, º West) (º South, º East) 90 º Prime Meridian South Absolute City Locations • • • • 23º N, 90º E 46º N, 76º W 4º N, 74º W 35º S, 149º E • • • • Dhaka, Bangladesh Ottawa, Canada Bogotá, Colombia Canberra, Australia Absolute City Locations • • • • 33º N, 44º E 52º N, 0º 7º N, 80º E 35º S, 59º W • • • • Baghdad, Iraq London, England, UK Colombo, Sri Lanka Buenos Aires, Argentina Time Zones • Degrees around world? • 360 • Hours in a day? • 24 • # of degrees per time zone? = • 15 Map Distortions 1.The extent of space between two objects or places; an intervening space 2. The position of one point in relation to another 3. A form or condition in which something may exist or appear 4. A roughly bounded part of the space on a surface; a region 1. Distance 2. Direction 3. Shape 4. Size/Area Map Elements 1. 2. 3. 4. Shows Direction Explains Content Shows Distance Explains Subject 1. 2. 3. 4. Compass Rose Legend/Key Scale Title Topographic Maps • Map showing the relief features of the earth’s surface – Variation, or difference in elevation of an area • Contour Interval – Difference in elevation between two contour 200 lines 240 Important Lines of Latitude Arctic Circle 66½°N Tropic of Cancer 23½°N Equator Tropic of Capricorn 0° 23½°S Antarctic Circle 66½°S Prevailing Winds Polar Easterlies Westerlies Pressures High latitudes Middle Latitudes Northeasterly Trade Winds Low Latitudes Southeasterly Trade Winds Low Latitudes Westerlies Polar Easterlies Middle Latitudes High latitudes Polar High Sub Polar Low Subtropical High Equatorial Low Subtropical High Sub Polar Low Polar High The Earth’s Structure Inside The Earth The Crust The Mantle Inner Core Outer Core Plate Behaviors 1. Plates move towards each other 2. Plates move away from each other 3. Plates moving past and against each other 1. Convergent Subduction & Collision 2. Divergent (Spreading) 3. Translation Climates • Vernon Hills • • Amazon Rainforest • • Five Factors: • • • • • • Determined by • Elevation Humid Continental Tropical Wet/Humid Tropical Latitude Ocean Currents Wind Currents Topography (Rain Shadow) Elevation Highland Culture • A new way of doing something • A culture changes through its meeting with another culture • The spread of an idea or culture trait • Belief that one’s own ethnic group is superior • Innovation • Acculturation • Diffusion • Ethnocentrism R&D Stairway to Economic Stability Ser. Ind. C.F. S.F. H&G Primary S e c o n d a r y T e r t i a r y Mang. Q u a t e r n a r y Developed vs. Developing DEVELOPED • Urban • Service (Tertiary) based economy • Strong Infrastructure • Low Growth Rate • Middle Class • • • • • DEVELOPING Urbanizing (Rural -> Cities) Agricultural (Primary) Base economy Poor infrastructure High Growth Rate Income Gap Age-Sex Pyramids World Population • Why is the earth’s population increasing the same amount each year despite a falling growth rate? – Exponential Growth (7 Billion) Types of Economies • Market Economy (Capitalism) – Consumers determine prices & production – Supply & Demand • Command Economy (Communism) – Gov’t determines prices & production • Mixed Economy (Socialism) – Aspects of both, gov’t control’s some industries Spheres of the Earth • All water on the earth • All land including ocean basins • All air surrounding the earth • All life on earth • Hydrosphere • Lithosphere • Atmosphere • Biosphere Layers of the Earth TOP SOIL SUB-SOIL WEATHERED ROCK SOLID ROCK Hydrologic Cycle Condensation Precipitation Evaporation/Transpiration Landforms • Thin piece of land connecting two larger pieces • Thin piece of water connecting two larger bodies • Piece of land surrounded by water on three sides • Chain of Islands • Isthmus • Strait • Peninsula • Archipelago Deforestation • Causes – Subsistence Farmers – Slash & Burn – Commercial Logging – Livestock Grazing – Roads (Fishbone) • Effects – Global Carbon Cycle – Global Warming – Extinct Species (50%) – Medical losses Political Instability Spanish Rule Independence Oligarchy Junta Democracy Simon Bolivar – Led many independence movements Oligarchy – Rule by the few Junta – Military Leaders (Caudillo – strong man) Coup – Government Takeover Guerrillas – Paramilitary forces