* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Physical Geography: A Living Planet
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
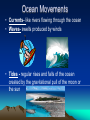
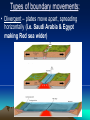
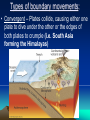
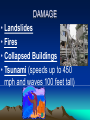
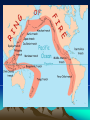
Chapter 2 Physical Geography: A Living Planet CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY • Originally suggested by Francis Bacon in 1620 • Presented theory in 1912 by Alfred Wegner of Germany • Theory states that all continents were once a super continent that divided and slowly drifted apart Where are we? • 93,000,000 miles from the Sun • 3rd Planet in from the Sun • 24,900 miles in circumference and 7900 miles in diameter • Only planet in Milky Way solar system that can sustain human life THE MILKY WAY • • • • Our Solar system consist of the sun 8 planets 1 dwarf planet (Pluto) Other celestial bodies that orbit the sun – Comets > spheres covered with ice and dust that leave trails of vapor as they race through space – Asteroids > large chunks of rocky material found in space • By size: Pluto (dwarf), Mercury, Mars, Venus, Earth, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter Section 1: The Earth Inside and Out • 1. The earth is the only living planet… • Continents – landmasses above water on earth • 2. The earth consists of plates that float… • 3. The theory of continental drift explains the formation of continents Inside the Earth Core – center of the earth (inner core- liquid iron and nickel; outer core – solid iron and nickel) Mantle – several layers surrounding the core Crust – thin layer of rock at the earth’s surface Biosphere • The part of the earth where plants and animals live (atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere) On and Above the Earth • Atmosphere – layer of gases surrounding the earth (contains oxygen, protects the earth from radiation and space debris, and provides a medium for weather and climate Lithosphere • Solid rock portion of the earth (includes crust and uppermost mantle, ocean floor, etc.) Hydrosphere • Made up of water elements of the earth (oceans, seas, rivers, lakes and water in the atmosphere) Section 2: Bodies of Water and Landforms • Human Perspective – The earth is unlike any other observable planet in our solar system. It is a living planet. – Where there is water there is LIFE. Section 2: Bodies of Water and Landforms The ocean is interconnected and covers over 70% of the earth. Divided into 4 main parts. Pacific (largest), Atlantic, Arctic and Indian Ocean Movements • Currents- like rivers flowing through the ocean • Waves- swells produced by winds • Tides - regular rises and falls of the ocean created by the gravitational pull of the moon or the sun MOTION OF THE OCEAN • The ocean distributes heat. • Winds blow over the ocean and are either heated or cooled by the water, moderating the temperature of the air over the land. Hydrologic (water) Cycle • The water on earth is continuously circulated between the atmosphere, the oceans, and the earth LAKES, RIVERS, & STREAMS • Lakes hold more than 95% of all fresh water on earth. • Rivers and streams move water to or from larger bodies of water. LAKES, RIVERS, & STREAMS • Saltwater lakes are created when creeks & rivers carry salts into a lake, and there is no outlet to carry the salt away. Largest: Caspian Sea (West Asia) • Drainage Basin Area drained by a major river and its tributaries Ground Water– water held in the pores of rocks Water Table – the rim level at which rocks are saturated Oceanic Landforms (topography) • The ocean floor and the continents have a continental shelf and slope • The ocean floor is similar to the land above water. continental shelf Continental Shelf • Earth’s surface from the edge of a continent to the deep part of the ocean Continental Landforms • Naturally formed features on the surface of the earth are landforms Topography & Relief • Relief refers to the difference in elevation of a landform from lowest to highest point – Mountains, hills, plains, canyons • The combination of the surface shape and composition of the landforms and their distribution in a region > topography • Topographic Maps show the landforms with their vertical dimensions and their relationship to other landforms. Section 3: Internal Forces Shaping the Earth • The earth’s crust consists of number of tectonic plates • tectonic plates enormous moving pieces of the earth’s lithosphere – Spreading; subduction; collision; sliding past each other in a shearing motion Movement of the plates produces earthquakes and volcanoes • Fault – fracture in the earth’s crust where plates move past each other Types of boundary movements: • Divergent – plates move apart, spreading horizontally (i.e. Saudi Arabia & Egypt making Red sea wider) Types of boundary movements: • Convergent – Plates collide, causing either one plate to dive under the other or the edges of both plates to crumple (i.e. South Asia forming the Himalayas) Types of boundary movements: • Transform – plates slide past each other (i.e. San Andreas Fault in California) Volcanoes – crack in the earth’s surface where magma and gases pour out Benefits > fertile soil & energy Lava – magma that has reached the earth’s surface • Earthquake – Violent movement of the earth as the plates grind or slip past each other at a fault – 95% around Pacific Rim (Ring of Fire) • Along plate boundaries • Seismograph – measures the size of the waves created by and earthquake – Largest Earthquake measured> Kermadec Island, 8.9 Epicenter • Point directly above the focus of an earthquake on the earth’s surface • Richter Scale – uses information collected by seismographs to determine the strength of an earthquake DAMAGE • Landslides • Fires • Collapsed Buildings • Tsunami (speeds up to 450 mph and waves 100 feet tall) Tsunami • A giant wave in the ocean caused by an underground earthquake The Ring of Fire • The most active volcano and earthquake zone on earth “Hot Spots” • Volcanoes that are far from the margins of the tectonic plates are located on “Hot Spots”. • Hot springs & geysers are other features that indicate areas where the crust is thin. External Forces Shaping the Earth Human Perspective: In Egypt, a seasonal dry wind is called Khamsin (50) for the number of days the season occurs. These wind-driven sandstorms cause serious problem for the people of the region. External Forces Shaping the Earth • Weathering and erosion alter the surface of the earth • Weathering – physical and chemical processes that change the characteristics of rock on or near the earth’s surface • Sediment – Small pieces of rock created by weathering (mud, sand or silt) • Mechanical Weathering – processes that break rock into smaller pieces (doesn’t change the composition of rock, but the size) Example: road construction - 4 causes > human activity, plants, frost, ice crystal in cracks of rocks • Chemical Weathering – occurs when rock is changed into a new substance as a result of interaction between elements in the air or water and minerals • (example – iron rusting) Erosion • Occurs when weathered material is moved by the action of wind, water, ice and gravity Water Erosion • The motion picks up loose material and moves it downstream • Delta – sediment is deposited in a fan-like landform when a river enters an ocean Wind erosion • Wind speeds have to reach 11 mph before fine sediments can be moved. • Depending on the types of wind, different types of landforms can be formed: –Loess, sand dunes, rock structures. wind erosion Loess – windblown silt and clay sediment that produces very fertile soil Glacial Erosion • Glacier - a large, longlasting mass of ice that moves because of gravity (Form in mountainous regions) • Glaciation – changing of landforms by slowly moving glaciers • Moraine – rocks left behind from a glacier that form a ridge or hill BUILDING SOIL HUMUS Organic material in the soil. Esker > snakelike ridge Created by melted ice Kettle > depression in the ground created by blocks of trapped ice in the sediment that melts. They can fill with water to form lakes. • Weathering and erosion help form soil. Soil consist of a loose mixture of weathered rock, organic matter, air, and water that supports plant growth • Factors that determine soil fertility: – Parent Material – Relief – Organisms – Climate – Time • The variety – and the climates in which they are found – determine the types of vegetation that can grow in a location. Agricultural activities, such as farming, ranching, and herding, depend on this complex relationship.