* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mapping the Ocean Floor
Sea level rise wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
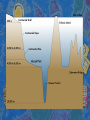
Mapping the Ocean Floor Essential Questions What are some of the features found on the ocean floor? What technology is used to map the ocean floor? What are some of the features found on the ocean floor? Continental Shelf A flat, wide margin is found around every continent The average width of a continental shelf is 70 kilometers Slopes at an angle of 0.1°, or 1.7 meters per kilometer Continental Slope The continental slope is about 16 kilometers wide, on average, and descends to a depth of about 2.4 kilometers The slope of the ocean floor becomes much steeper, typically a 4° slope, or 70 meters per kilometer. is grooved by submarine canyons and gullies. Continental Rise The slope moderates to a mere degree or two from horizontal which is called the continental rise Submarine Canyon is a steep-sided valley on the sea floor of the continental slope cutting the continental slopes have been found at depths greater than 2 km below sea level. Oceanic Trench Is where an oceanic crust plate begins to descend beneath another oceanic crust plate Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km from a volcanic arc. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 10,911 m below sea level. Abyssal Plain The abyssal plain, which is the deepest, most level part of the ocean, is found where the continental rise ends, at a depth of about 4 kilometers. The abyssal plain is dotted with thousands of small, extinct volcanoes called abyssal hills. Mid-Ocean Ridge a long, undersea mountain chain that usually extends down the middle of the ocean The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, for example, snakes down the middle of the Atlantic most of the way from the North Pole to Antarctica. Rift Valley Along the center of the mid-ocean ridge is the rift valley, a deep V-shaped notch. From this valley, new oceanic crust is constantly being extruded from Earth's mantle by processes not yet fully understood. In the case of the Mid-Atlantic rift valley, one sheet flows east and the other west, each moving at about half an inch per year. This causes sea floor spreading. Guyot is an isolated underwater volcanic mountain, with a flat top over 200 meters (660 feet) below the surface of the sea. the diameters of these flat summits can exceed 10 km. Seamount is a mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface, and thus is not an island. these are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of 1,000–4,000 metres depth Hydrothermal vent is a fissure in a planet's surface from which geothermally heated water issues are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart, ocean basins, and hotspots Interesting facts Mauna Kea, Hawaii, rises 33,474 feet from its base on the ocean floor; only 13,680 feet are above sea level The ocean ridges form a great mountain range, almost 64,000 km long, that weaves its way through all the major oceans. It is the largest single feature on Earth Deepest point - 36,198 feet in the Mariana Trench in the western Pacific. What technology is used to map the ocean floor? Historically For hundreds of years, the only way to measure ocean depth was the sounding line, a weighted rope or wire that was lowered overboard until it touched the ocean floor. Not only was this method time-consuming, it was inaccurate; ship drift or water currents could drag the line off at an angle, which would exaggerate the depth reading. It was also difficult to tell when the sounding line had actually touched bottom Present Day SONAR – acronym for SOund Navigation And Ranging is a technique that uses sound propagation – SONAR waves are sent from a ship and the time for the waves to return is measured – the farther the distance the longer the time, the shorter the distance the smaller the time Sea 3-D: Charting the Ocean Floor - KQED QUEST http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1h4 vaERMNbs 5:59 Oceanfloor Legacy http://video.google.com/videoplay?doci d=862857452234843312# 28: America's New Frontier http://video.google.com/videoplay?doci d=-7837963317498620058# 27:30