* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Abyssal Plain:
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
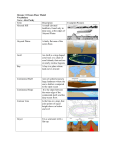
Oceans Study Guide Abyssal Plain: the deepest area of the ocean floor Continental Rise: area of transition between the abyssal plain and the continental slope that is covered with thick sediment Continental Shelf: rather level area of the ocean floor that is covered with thick sediment and links the shoreline with the continental slope Continental Slope: feature of the ocean floor that is covered with thick sediments and spans the change in depth between the continental shelf and the continental rise Ocean Trench: Mid-Ocean Ridge: Seamount: a canyon in the deepest area of the ocean floor mountain range found along the ocean floor (Only the peaks, if any, of the mid-ocean ridge are visible above the ocean's surface.) an underwater sea mountain Depth: measurement from the ocean's surface to the floor in one given spot Environment: The surroundings or conditions an organism lives in. Ecosystem: network of the interactions between organisms and their environment (It has both living and nonliving components.) Gulf Stream: the major current on the Eastern United States coast that travels north from the equator (It affects the temperature and weather of this region.) Ocean: one of seven large bodies of salt water that cover about 70% of the Earth's surface Phytoplankton: single-celled plant-like and bacteria plankton which float on the ocean’s surface, producing much of the Earth’s oxygen and serving as one of the basis for the marine food web Plankton: tiny open-water plants, animals, or bacteria that are transported by water currents and tides Nekton: marine organisms that have the ability to swim or move against the current Benthic: organisms that live on the bottom of the ocean that are not freefloating Salinity: measure of the concentration of dissolved salt in water Tide: rhythmic movement of water on the Earth's surface that is caused by the moon's Current: a "river" of water caused by temperature changes and the Earth's rotation that moves quickly through a larger body of water