* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside the Earth
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
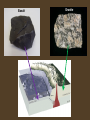
Inside the Earth Evidence • Geologists can’t observe Earth’s interior directly. • Must observe indirectly through seismic waves. • Caused by earthquakes, seismic waves are vibrations of matter (kinetic energy) that travel through the various mediums of earth at different rates. • By measuring recording seismic waves at multiple locations on earth, scientist have been able to infer the density and composition of earth’s interior. Composition • Crust • Mantle • Liquid Outer Core • Solid Inner Core The Crust • Outer layer • 5-40 km thick • It is thinnest beneath the ocean and is thickest below a mountain. • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense, made of basalt) – Continental (less dense, made of granite) Basalt Granite The Mantle • About 3,000 km thick • Mantle is soft rock and flows freely like melted plastic. • Temperature and Pressure increase with depth. • Temperatures range from 870°C to 2,200°C • Convection currents Convection video: http://education.sdsc.edu/optiputer/flash/convection.htm Liquid Outer Core • Consists of liquid iron and Nickel. • Currents in the liquid spin to generate the earth’s magnetic field. • Can be as hot as 5,000°C Earth’s Magnetic Field Solid Inner Core • An extremely dense ball of solid metal. • The inner cores and out cores together are just slightly smaller than the Moon • So much pressure that the liquid iron and nickel can not spread out to form a liquid. Scientist think the spinning of the inner core is what causes the currents in the outer core, and thus, Earth’s magnetic field. Earth’s Layers • How are the earth’s layers similar to an egg? • Shell=crust • Egg white=mantle • Yolk=core Upper Layers of the Earth • Lithosphere - rigid outer layer - including the crust and uppermost mantle. • Asthenosphere – rock material that flows slowly (Ductile - like hot asphalt) - including the lower mantle Tectonic Plates • Earth’s crust is broken into about 19 pieces • These plates move on top of the asthenosphere • Throw yo hands up for the layers of the Earth !!! Earth’s Layers Video