* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
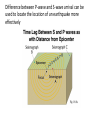
Earthquake Amplitude Magnitude and Intensity. • Which of the stations is farthest from the epicenter? • Which of the stations is closest? • How do you know? Difference between P-wave and S-wave arrival can be used to locate the location of an earthquake more effectively Difference between p- and s-waves can be used to track location Collect data from at least 3 seismograms from an earthquake Use the Time-Distance graph to find distance from epicenter for each seismogram Use each distance to draw a circle of possible epicenters The actual earthquake epicenter is found at the spot where all 3 intersect Need a minimum of 3 stations to isolate location (and the more the better) • Measuring the size of the earth quake • 1- Where did the earthquake occur? • 2- How big was the earthquake? Modified Mercalli Scale Mercalli Scale • Mercalli Scale a seismic scale used for measuring the intensity of an earthquake • the scale are based on observed structural damage • based on observed effects The Richter Scale • The first widely-used method • Based on amplitude of the largest wave recorded and the distance between the earthquake and the seismometer • Two pieces of information used to calculate size of Earthquake on the Richter Scale: a) Deflection of seismometer, b) b) distance from source (based on P & S wave arrivals) The Richter Scale • Earliest measure of earthquake size • Easy to measure • Empirical -no direct tie to physics of faulting The Richter Scale • Magnitude – varies by powers of 10 – One point increase in magnitude means that the amplitude of the seismic wave is 10 times greater. – Example - Mag 5 Mag 6 • The seismic wave is 10x bigger) • Energy released ( 31 X more energy ) • How much bigger is the amplitude of a 8.3 magnitude earthquake compared to 4.3 magnitude earthquake? • 8.3-4.3 = 4 104 = 10,000 bigger • And on million times more energy •https://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=05kBRmJh3F8 • Richter scale, do not provide accurate estimates for large magnitude earthquakes • Measures how much energy is released. • Today we use Moment magnitude scale, abbreviated MW • works over a wider range of earthquake sizes and is applicable globally • moment magnitude (MW) scale is based on the total moment release of the earthquake • product of the distance a fault moved and the force required to move it • about the same as Richter magnitudes • (MW) can read ‘magnitude 8 and greater events accurately • sudden slip of one part of the Earth's crust, relative to another, along a fault surface. • Thrust fault scarp at El Asnam, Algeria • Connecting Earthquakes and Faults • Connecting Earthquakes and Faults -Interested in the amount of displacement between points • Link between ( magnitude) energy with the severity of fault rupture • The seismic moment (Mo) analysis of seismic waves, directly proportional to the extent of the actual fault rupture • 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake, Taiwan • How big is an earthquake? • Depends on how big a patch of the fault breaks • 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake, Taiwan • magnitude scales are logarithmic • The area of the circle is proportional to the energy of an event at moment magnitude +1 versus moment magnitude +2. • https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=HL3KGK5e qaw "drop, cover and hold on" • a consensus has been building that "drop, cover and hold on" is a more appropriate method for developed countries like the U.S., where there are the best constructing codes triangle of life • Before: Survival supplies • Identify safe zones inside and outside • Evacuation plan and plan where to meet • During: Inside-Seek cover under table, desk, • Outside- Face down away from buildings, trees, powerlines • After: Stay out of damaged buildings, be prepared for aftershocks • Mass damper- helps compensate for building movement • Active tendon system- helps compensate for building movement • Base isolators- shock absorbers that stop the passing of seismic waves • Cross braces-counteracts the pull and push stresses • Flexible pipes- prevent water and gas lines from rupturing