* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RESPIRATION
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
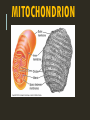
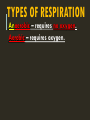
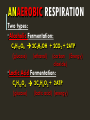
RESPIRATION RESPIRATION 1. The process of breaking down food molecules to release energy. 2. Converts the energy in glucose to ATP 3. Occurs in the mitochondria. MITOCHONDRION TYPES OF RESPIRATION Anaerobic – requires no oxygen. Aerobic – requires oxygen. ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION Two types: Alcoholic Fermentation: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + 2ATP (glucose) (ethanol) (carbon (Energy) dioxide) Lactic Acid Fermentation: C6H12O6 2C3H6O3 + 2ATP (glucose) (lactic acid) (energy) ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION Occurs when bacteria and fungi (yeast) break down plants (Ex: vegetables and fruit) and release alcohol or vinegar. LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION -Occurs in muscles – due to a lack of oxygen. -Leads to a buildup of lactic acid in muscles causing soreness. AEROBIC RESPIRATION C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36ATP Glucose) (oxygen) (carbon (water) (energy) dioxide) Occurs in both plants and animals Much more efficient than anaerobic respiration. THE PROCESSES OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION See you next time!













![fermentation[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008290469_1-3a25eae6a4ca657233c4e21cf2e1a1bb-150x150.png)





