* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification & Origin of Life - mvhs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
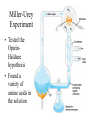
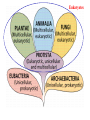
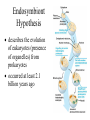
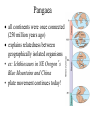
Classification & Origin of Life AP Biology Unit 4 Characteristics of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Metabolism, Growth, & Development Reproduction Response to Environment Genetic Information that can be passed on, evolution Physical order/ highly ordered system • • • • • • Is fire living? NO Is a virus living? NO Is a prion living? NO Origin of Life on Earth • Scientific evidence indicates that Earth formed 4.6 billion years ago (bya) • First evidence of life on Earth is from fossils that are 3.5 billion years old. • There are multiple theories and models about how living things/cells may have first appeared. General Sequence of Events • Small organic molecules (like amino acids and nucleotides) form from abiotic factors. • Small organic molecules join together into biomolecules that can replicate, store and transfer info • Molecules become surrounded by a membrane – “protobionts” • Cellular processes develop Oparin-Haldane Hypothesis (1920s) • Hypothesis about how early organic compounds were synthesized • Said Earth had a reducing atmosphere – CH4, NH3, and H2 present in atmosphere (no O2) – H2O in ocean – Electricity added (provided electrons) – lightning This would produce fatty acids and amino acids Miller-Urey Experiment • Tested the OparinHaldane hypothesis • Found a variety of amino acids in the solution Additional Experiments • Oro (1961) • Repeated experiments similar to MillerUrey – Produced amino acids, sugars, nucleotides • All of these experiments show it is possible to synthesize organic molecules from abiotic sources. “RNA World” Hypothesis • Proposes that RNA was the first genetic material (not DNA). • self-replicating RNA carried out catalytic activities (because no protein or DNA yet) • RNA found to have many catalytic properties that support this hypothesis: – ex. microRNAs – ex. Ribozymes (RNA catalysts), Ribosomes Classification Method: 5 Kingdoms • Monera (Prokaryotes) • Protista – Euglena, Amoeba, etc. • Plantae • Fungi • Animalia Classification: 3 Domains • 3 Domains are Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya Monera Kingdom is divided into Bacteria and Archaea Branching pattern is based on rRNA sequence comparison Former branching pattern based on behavior placed Archaea as most related to the Origin of Life (hence the name Archaea) Eukaryotes Presumed Development of Ancestor of Eukaryotes Endosymbiosis happens (chloroplasts) Endosymbiosis happens (mitochondria) Ancestor of eukaryotic cells (mixture of bacteria and archaea) Earliest common ancestor of all living things Domains • Bacteria – Unicellular – Live at moderate environments – Prokaryotes • Archaea – Unicellular – Live at extreme environments (temperature, salinity, etc) – Prokaryotes Domains • Eukarya – Multi or unicellular – Eukaryotes Endosymbiont Hypothesis describes the evolution of eukaryotes (presence of organelles) from prokaryotes occurred at least 2.1 billion years ago Evolution of Colonies • Colonies evolved before multicellular organisms • Important for the eventual evolution of multicellularity multicellularity occurred at least 1.5 billion years ago • Benefits of colonies? – Shared tasks but each organism is independent Pangaea all continents were once connected (250 million years ago) explains relatedness between geographically isolated organisms • ex: Ichthiosaurs in NE Oregon’s Blue Mountains and China • plate movement continues today! Classification Overview • Cell Types: – Prokaryotes • No nucleus • No cytoskeleton • No Membrane-bound organelles – Eukaryotes • Both unicellular and multicellular • Nuclei, cytoskeleton, and organelles present Monera Fun fact: There are more bacteria living in you than your own body cells! Monera • • • • Bacteria (Prokaryotes) Unicellular Most have a cell wall Can be photosynthetic Protista Fun Fact: Euglena “Red tide” is caused by reddish colored protists that grow too fast and make the ocean look pinkish. Amoeba Protista • • • • • Mostly Unicellular Many are colonial Can be motile Can be photosynthetic (autotrophs) Some have a cell wall Fungi Fun fact: The largest living organism might be a fungus– it is a species of Armillaria bulbosa that is around 1500 years old and extends across 35 acres of land in northern Michigan! Fungi • • • • • Unicellular or Multicellular Eukaryote Non-motile Heterotrophs– NO PHOTOSYNTHESIS Have a cell wall Plantae Carnivorous Plant Fun Fact: Rafflesia arnoldii is the largest flower in the world • It can grow up to 3 feet across and weigh 15 pounds • It emits a smell similar to rotting meat Plantae • • • • • Multicellular Autotrophs Non-motile Eukaryotes Have a cell wall (cellulose) Animalia Fun Fact: The African porcupine has quills that are about a foot long and ¼ inch in diameter. Animalia • • • • • Multicellular Heterotrophs Eukaryotes Most are motile No cell wall