* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benchmark 1st 9 weeks st guide with answers
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
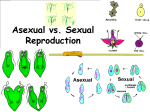
Binomial nomenclature Aristotle Genus & species Taxonomy - Linnaeus Study of classification Homo sapiens First name cap, 2nd lowercase, italicize or underline Protists Fungus Eukarya Plants Bacteria Animals Omain ingdom hylum Archaea & lass rder amily enus pecies Process in which an organism maintains stable internal conditions study of living things. Autotroph producer heterotroph Plants Process in which one organism eats another to obtain energy. Overlapping food chains in an ecosystem Grass –Rabbit--- eagle consumer animals 3rd level Living thing the producer level consumer No Nucleus Basic unit ofStructure Has a and Function of living things nucleus 10% 2nd levelConsumer 1st level consumer PRODUCER SUN energy moves up - only 10% Nonliving living things Tree, dog, Soil, water, temp Study of living things and how they interact with each other and their population growth environment. limits Food, water, shelter evaporation – liquid to gas; condensation – back to liquid, precipitation – becomes asexual – new DNA one splits off heavy falls as rain, sleet, snow, or hail. All living things have carbon and plants take in CO2 and give back Oxygen, we do the opposite Nitrogen is “free” in the air, but must be fixed and when living things die their nitrogen goes back into the cycle . Ribosomes and dna sexual – tube forms and genetic info is exchanged. must be fixed from air to useable form eukaryotic Lightning and bacteria prokaryotic Animal like heterotrophs unicellular, eukaryotes, heterotrophs and autotrophs, sexual and asexual reproduction Plant like = photosyn. Fungus like – use spores Flagella (euglena) Pseudopods amoeba according to how they move. Cocci (round)m spirilla (spiral), and bacilli (rod) Virus has dna and a protein coat, bacteria has dna also and is alive – does not need host Virus hijacks and needs a host, a bacteria can reproduce sexually- conjugation and asexually – binary fission Capsid outer covering of protein coat Cilia paramecium DNA