* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformation_Slides_000
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
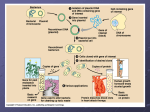
Transformation Slides Cellular organelles targeted with FPs Human cell stained with two different fluorescent proteins to visulalize cytoskeletal components. Transfected with GFP-tubulin / mCherry actin (Ben Giepmans) C Elegans transfected with GFP tubulin construct (Susan Kline) Transcription / Translation Campbell What is Transformation? Bacterial chromosome Uptake of foreign DNA, often a circular plasmid Plasmid Bacterial chromosome Plasmid Bacteria now express cloned fluorescent protein (transcription of gene and translation of mRNA to protein at ribosomes). Allow bacteria to grow for 1-3 days on plate with ampicillin. What is a plasmid? • A small circular piece of DNA that replicates separately from the main bacterial chromosome • Originated in bacteria to allow survival in specific environmental conditions • May express antibiotic resistance gene or be modified in the lab to express proteins of interest How are plasmids engineered? DNA Plasmid Vector Host DNA fragments (i.e. coral or jellyfish FP coding DNA) Ligate (paste) fragments into cut DNA vector Cut genomic DNA into fragments + Cut plasmids open with restriction enzymes End result: Plasmid containing FP gene FP transformation procedure 1. Suspend bacterial colonies in CaCl2 2. Add plasmid DNA 3. Place tubes on ice for 10 min 4. Heat-shock at 42°C for 45 seconds & place on ice again for 2 min 5. Plate out bacteria READ THE INSTRUCTIONS AT YOUR LAB TABLE! Materials Checklist 1 tube of CaCl2 on ice 2 empty microtubes 1 waterproof pen 4 disposable transfer pipette (or you can use p20’s with yellow tips) Innoculating loops OR sterile tips 2 cotton swabs tape for sealing plates after innoculation 1 LB plate 2 LB/AMP plates Ice bucket (cup with ice and water) One tube of plasmid labeled either PM1 or PM2 on ice. Class or lab station waste containers Why calcium chloride? Ca++ Ca++ O P O O • Transformation solution = CaCl2 • Positive charge of Ca++ ions shields negative charge of DNA phosphates so the plasmid DNA can more easily move through the cell membrane O CH2 Base O Sugar O Ca++ O P O Base O CH2 O Sugar OH Why ice and heat? • Incubate on ice slows fluid cell membrane • Heat-shock increases permeability of membranes Why Ampicillin? • Ampicillin inhibits cell growth. Only cells that can inactivate the ampicillin around them will grow. • Ampicillin resistance fluorescent protein gene is tied to (expressed with) the • Ampicillin is a selection mechanism that only allows transformed bacteria to grow on the plate How are Fps used by scientists? • Researcher wants to study a protein of interest, perhaps a protein that is part of a pathway such as respiration. • But how does the researcher visualize the protein and find out where in the cell it is expressed? http://www.conncoll.edu/ccacad/zimmer/GFP-ww/GFP4.htm How are Fps used by scientists? • The FP gene is inserted into the plasmid right after the gene for the protein, before the stop codon. • The protein of interest AND the FP are translated together. • The FP can be seen and measured, even though the protein of interest cannot be seen. Anytime the protein of interest is made in the cell, the FP will also be made. http://www.conncoll.edu/ccacad/zimmer/GFP-ww/GFP4.htm