* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.1 & 4.2C Ocean Life PPt
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Blue carbon wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine life wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
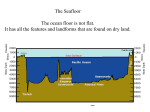
Ch 4.1/4.2C Messana Ocean Life **3 Categories: 1. Bottom-Dwellers (Benthic) 2. Floaters 3. Swimmers Which is which? -> **All marine organisms live in a HABITAT = An ENVIRONMENT that has all the NECESSARY REQUIREMENTS for an organism to LIVE!! ESTUARIES (at coastlines) Area where FRESH WATER from rivers & SALT WATER from the ocean MIXES! SALINITY changes constantly Salinity is lower in open ocean, higher in rivers/lakes Breeding grounds for many organisms; organisms have specific adaptations WETLANDS Along edges of ESTUARIES WET, SWAMPY AREAS that are FLOODED with water 2 Types: 1.)SALT MARSHES ~ Coastal Wetlands in COOL AREAS Nutrient rich SOIL Thick grasses 2.)MANGROVE FORESTS ~ Coastal Wetlands in WARM AREAS Found closer to the EQUATOR (Southern US) Mangrove shrubs & trees with thick roots extending into water Human Harm to Wetlands: - clearing of land - pollution from industry/shipping WETLAND LIFE Migrating BIRDS use these areas as REST STOPS Habitat for WILDLIFE Grasses & root systems keep SHORELINE from washing away, hold sediment in place ORGANISMS break down the GRASSES, return NUTRIENTS to the MARSHES Intertidal Zone Area of coastline between HIGH & LOW tide The HABITAT at the EDGE of the ocean DRY & EXPOSED to SUNLIGHT during LOW TIDE 50 % of the WORLD’S POPULATION live within 50 miles of the COAST PROTECTION of the SHORELINES: 1) Improve sewage treatment plants 2)Laws to restrict dumping 3) Set up Shoreline Sanctuaries OCEAN ENVIRONMENTS – AWAY FROM THE COAST WATERS near the SHORE~ 1.)Supports the greatest variety of life (=BIODIVERSITY) of any part of the ocean BACTERIA, PROTISTS, PLANTS, ANIMALS 2.) Continental SHELF area 3.) SUNLIGHT reaches the bottom 4.) Many NUTRIENTS entering from the land 5.) TEMPERATURE & SALINITY fairly CONSTANT CORAL REEFS Found in TROPICAL WARM WATERS A build-up of LIMESTONE remains after the CORAL ORGANISM dies ALGAE live inside the reef & PRODUCE FOOD Contains over 25% of all species of ocean life ENDANGERED area due to POLLUTION & OVERFISHING Australia’s GREAT BARRIER REEF Can be seen from outer space! Kelp Forests Found in COLD WATERS Large areas of SEAWEED Uses SUN to make food via photosynthesis Habitat for many ORGANISMS EX: fish, otters, snails, crabs, worms OPEN OCEAN Environments Change w/ DEPTH 1) LIFE is more SPREAD OUT 2) NUTRIENTS sink down 3) SUNLIGHT reaches ONLY the top 4) NO SHELTER for ORGANISMS SURFACE ZONE 1) Top 200 meters 2) SUNLIT 3) PHYTOPLANKTON Plant-like microscopic FLOATING organisms; do photosynthesis to convert SUNLIGHT & CO2 to GLUCOSE & O2 4) ZOOPLANKTON – animal-like; feed on the phytoplankton 5) OCEAN ANIMALS - eat the zooplankton DEEP ZONE 1) DARK, COLD, HIGH PRESSURE 2) NO PLANTS 3) PREDATORS eat PREY OR food comes down from above (nutrients, dead organisms) 5) Organisms may GLOW in the dark = BIOLUMINESCENCE 6) Small eyes or none at all, prehistoric-looking 7) Animal communities found on deep ocean floor = HYDROTHERMAL VENTS Cold water goes into cracks in the crust & gets HEATED BY MAGMA BACTERIA = base of the food chain here, no sunlight or plants needed