* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Klebsiella pneumoniae
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
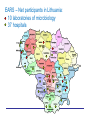
CHOICE OF ANTIBIOTICS IN THE VIEW OF DEVELOPING ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE Dr. Jolanta Miciulevičienė Vilnius City Clinical Hospital National Public Health Surveillance Laboratory BARN 3rd Workshop ʺPrevention of Surgical Site Infectionsʺ Visby, 2012 Discovery of Penicillin Changes the History of Medicine In 1928 Sir Alexander Fleming, a Scottish bacteriologist, left a Petri dish with staphylococci uncovered. When he returned, he noticed that there was mold growing on it. Upon further examination, he saw that the area around the mold had no bacteria growing. Fleming concluded that the mold was releasing a substance that was inhibiting bacterial growth. He grew a pure culture of the mold and discovered that it was a Penicillium, now known to be Penicillium notatum. Antimicrobial resistance • Soon after the introduction of the penicillin into clinical practice, the fact that the development of antibiotic resistance would be a problem became apparent. • Resistance to penicillin in some strains of Staphylococcus was recognized almost immediately after introduction of the drugs. Resistance to penicillin today occurs in as many as 90% of all strains of Staphylococcus aureus Antimicrobial resistance Most commonly, this refers to infectious microbes that have acquired the ability to survive exposures to clinically relevant concentrations of antimicrobial drugs that would kill otherwise sensitive organisms of the same strain. Resistant Nosocomial Pathogens • • • • • • • S.aureus (MRSA, GISA), Enterococcus spp. (VRE), E.coli (ESBL), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL, KPC), Enterobacteriaceae (MDR), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDR), Acinobacter baumannii (MDR). European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS – Net) Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. EARS – Net participants in Lithuania: 10 laboratories of microbiology 37 hospitals Number of blood-stream infections, Lithuania, 2007 – 2011 400 Number of BSi 350 300 Enterococcus spp. E.coli 250 K.pneumoniae 200 P.aeruginosa S.aureus 150 S.pneumoniae 100 50 0 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 Staphylococcus aureus: trends of invasive isolates resistant to meticillin (MRSA),Lithuania, 2007-2011 2007m. - 241/22, 2008m. - 280/31, 2009m. - 255/29, 2010m. – 257/36, 2011m. – 263/16 Staphylococcus aureus: proportion (%) of invasive isolates resistant to methicillin (MRSA), 2010 Klebsiella pneumoniae: trends of invasive isolates resistance to third-generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides, Lithuania, 2007-2011 Klebsiella pneumoniae: proportion (%) of invasive isolates with resistance to third-generation cephalosporins, 2010 Klebsiella pneumoniae: proportion (%) of invasive isolates with resistance to carbapenems, 2010 Number of K.pneumoniae blood stream infections, Lithuania, 2007-2011. Risk factors of developing bacterial resistance • Inappropriate prescribing (overprescribing); • Inappropriate selection of antimicrobial (broad spectrum cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, carbapenems, glycopeptides); • Prolonged administration of antimicrobial. Evidence Based • “Evidence-based medicine is the process of systematically finding, appraising, and using research findings as the basis for clinical decisions.” BMJ 1995;310:1122-1126 (29 April) William Rosenberg, Anna Donald Evidence-based Medicine: An Approach to Clinical Problem-solving Evidence-based medicine Reference: Cook PP, Catrou P, Gooch M, Holbert D. Effect of reduction in ciprofloxacin use on prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus rates within individual units of a tertiary care hospital. Journal of Hospital Infection. 2006; 64: 348-351 Setting: 731-bed tertiary care teaching hospital, Greenville, NC, USA. Evidence based medicine • Intervention Reduction - Active monitoring of oral and IV ciprofloxacin use. • Impact: Ciprofloxacin use decreased by 31.2% (p<0.0001). MRSA rates decreased from 59.6% to 54.2% (p=0.112). Correlation between ciprofloxacin use and MRSA rates (r=0.70; 95% CI -0.01-0.94 p=0.053). Evidence based medicine • Reference: Rahal JJ, Urban C, Horn D, Freeman K, Segal-Maurer S, Maurer J, Mariano N, Marks S, Burns JM, Dominick D, Lim M. Class restriction of cephalosporin use to control total cephalosporin resistance in nosocomial Klebsiella. JAMA, 1998;280(14): 1233-1237 • Setting: 500-bed university affiliated community hospital, Queens, NY, USA Evidence based medicine • Intervention Restriction - Hospital adopted antibiotic guidelines restricting routine cephalosporin use. • Impact: 80.1% reduction in hospital-wide cephalosporin use in 1996 compared to 1995. 44% reduction in incidence of ceftazidimeresistant Klebsiella infection and colonization throughout medical center (p<0.01) and 70.9% reduction in all intensive care units (p<0.001). Evidence based medicine • Intervention Restriction - Hospital adopted antibiotic guidelines restricting routine cephalosporin use. • Impact: 80.1% reduction in hospital-wide cephalosporin use in 1996 compared to 1995. 44% reduction in incidence of ceftazidimeresistant Klebsiella infection and colonization throughout medical center (p<0.01) and 70.9% reduction in all intensive care units (p<0.001). Take home message: Inappropriate selection and prolonged administration of antimicrobials Fluoroquinolones; Cephalosporins; Carbapenems; Glycopeptides. S.aureus (MRSA, GISA), Enterococcus spp. (VRE), E.coli (ESBL), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL, KPC), Enterobacteriaceae (MDR), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDR), Acinobacter baumannii (MDR). THANK YOU !