Antimicrobial Resistance Trends in the Province of British Columbia
... Percent of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates (CBSN) non‐susceptible to penicillin correlated with the utilization of β‐lactamase sensitive penicillins ........................................ 62 Defined daily rate of macrolide utilization............................................................. ...
... Percent of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates (CBSN) non‐susceptible to penicillin correlated with the utilization of β‐lactamase sensitive penicillins ........................................ 62 Defined daily rate of macrolide utilization............................................................. ...
Republic of Iraq Ministry of Higher Education And Scientific Research University of Baghdad
... properties that enhance their survival in phagocytes (carotenoids, catalase production), Immunological disguises (Protein A, coagulase), membranedamaging toxins that lyse eucaryotic cell membranes (hemolysins, leukotoxin, leukocidin), exotoxins that damage host tissues or otherwise provoke symptoms ...
... properties that enhance their survival in phagocytes (carotenoids, catalase production), Immunological disguises (Protein A, coagulase), membranedamaging toxins that lyse eucaryotic cell membranes (hemolysins, leukotoxin, leukocidin), exotoxins that damage host tissues or otherwise provoke symptoms ...
Capsular Polysaccharide Masks Clumping Factor A–Mediated
... repeat and the ability of the strains to clump in soluble Fg has been observed [5], a longer region R may allow region A of ClfA to project beyond the extracellular capsule layer [6]. ClfA plays an important role in S. aureus binding to platelets—an interaction that is critical to the induction of ...
... repeat and the ability of the strains to clump in soluble Fg has been observed [5], a longer region R may allow region A of ClfA to project beyond the extracellular capsule layer [6]. ClfA plays an important role in S. aureus binding to platelets—an interaction that is critical to the induction of ...
Cellulitis: A Review - UNM Hospitalist Wiki
... Cellulitis usually presents as an acute, spreading, poorly demarcated area of erythema. The skin findings in cellulitis follow the classic signs of inflammation: dolor (pain), calor (heat), rubor (erythema), and tumor (swelling). Additional clinical features may include dilated and edematous skin ly ...
... Cellulitis usually presents as an acute, spreading, poorly demarcated area of erythema. The skin findings in cellulitis follow the classic signs of inflammation: dolor (pain), calor (heat), rubor (erythema), and tumor (swelling). Additional clinical features may include dilated and edematous skin ly ...
here - UCLA Antimicrobial Stewardship Program
... All remain predictably susceptible to penicillin; resistance rates nationwide for Group B streptococci (S. agalactiae) are approximately 50% for erythromycin and 30% for clindamycin. Resistance rates for Group A streptococci (S. pyogenes) can be as high as 25% for erythromycin, 5% for clindamycin an ...
... All remain predictably susceptible to penicillin; resistance rates nationwide for Group B streptococci (S. agalactiae) are approximately 50% for erythromycin and 30% for clindamycin. Resistance rates for Group A streptococci (S. pyogenes) can be as high as 25% for erythromycin, 5% for clindamycin an ...
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE THREATS in the United States, 2013
... Antibiotic resistance is a worldwide problem. New forms of antibiotic resistance can cross international boundaries and spread between continents with ease. Many forms of resistance spread with remarkable speed. World health leaders have described antibioticresistant microorganisms as “nightmare bac ...
... Antibiotic resistance is a worldwide problem. New forms of antibiotic resistance can cross international boundaries and spread between continents with ease. Many forms of resistance spread with remarkable speed. World health leaders have described antibioticresistant microorganisms as “nightmare bac ...
Vancomycin: A 50-Year Reassessment
... ment in Reviews of Infectious Diseases (the predecessor to Clinical Infectious Diseases). The supplement was entitled “Reassessments of Vancomycin—A Potentially Useful Antibiotic” [5] and reflected a cautious, somewhat measured approach to the potential utility of vancomycin. That publication also m ...
... ment in Reviews of Infectious Diseases (the predecessor to Clinical Infectious Diseases). The supplement was entitled “Reassessments of Vancomycin—A Potentially Useful Antibiotic” [5] and reflected a cautious, somewhat measured approach to the potential utility of vancomycin. That publication also m ...
investigation of exudative epidermitis and ear necrosis
... Therefore, damage to skin can result in serious health consequences including dehydration and secondary infection. Lesions can be painful and are frequently linked to welfare concerns. Pig skin has economic value at slaughter in that it is an edible tissue but also can be used for leather and other ...
... Therefore, damage to skin can result in serious health consequences including dehydration and secondary infection. Lesions can be painful and are frequently linked to welfare concerns. Pig skin has economic value at slaughter in that it is an edible tissue but also can be used for leather and other ...
mrsa_protect - Texas Department of State Health Services
... issued clean clothing if pus or blood drains on their clothes. Bed sheets should be changed every other day or more often if pus or blood drains from the sore. If you are responsible for changing an inmates bandage… ...
... issued clean clothing if pus or blood drains on their clothes. Bed sheets should be changed every other day or more often if pus or blood drains from the sore. If you are responsible for changing an inmates bandage… ...
Bacterial Adherence to Surgical Sutures: Can
... suggest that as a biomedical device, surgical sutures exhibit an affinity for microbial adherence and colonization similar to that of other synthetic, implantable medical devices. Early studies demonstrated that adherence of microbial populations to suture material is highly variable, dependent on t ...
... suggest that as a biomedical device, surgical sutures exhibit an affinity for microbial adherence and colonization similar to that of other synthetic, implantable medical devices. Early studies demonstrated that adherence of microbial populations to suture material is highly variable, dependent on t ...
Surveillance of microbial resistance in European Intensive Care Units: a first
... benchmarking of antibiotic use and infection control practices. Keywords Intensive care - Antibiotic consumption - Microbial resistance - Infection control ...
... benchmarking of antibiotic use and infection control practices. Keywords Intensive care - Antibiotic consumption - Microbial resistance - Infection control ...
What is the nature and extent of antibacterial drug
... treatment duration. At the same time, there is a lack of access to effective antibiotics in some developing countries where the need for essential drugs is most immediate. In industrialized countries, around 80-90% of antibiotic use for humans occurs in the community and at least half of this is con ...
... treatment duration. At the same time, there is a lack of access to effective antibiotics in some developing countries where the need for essential drugs is most immediate. In industrialized countries, around 80-90% of antibiotic use for humans occurs in the community and at least half of this is con ...
Antibacterial Drug Resistance - WHO archives
... treatment duration. At the same time, there is a lack of access to effective antibiotics in some developing countries where the need for essential drugs is most immediate. In industrialized countries, around 80-90% of antibiotic use for humans occurs in the community and at least half of this is con ...
... treatment duration. At the same time, there is a lack of access to effective antibiotics in some developing countries where the need for essential drugs is most immediate. In industrialized countries, around 80-90% of antibiotic use for humans occurs in the community and at least half of this is con ...
Bacteria Battle Back - Addressing Antibiotic
... curb our ability to treat, cure and control infectious diseases. Antibiotics, often touted as one of the most important discoveries of modern medicine, are losing ground to bacteria that are now resistant to several drugs. The irony, of course, is that antibiotics developed to control bacteria have ...
... curb our ability to treat, cure and control infectious diseases. Antibiotics, often touted as one of the most important discoveries of modern medicine, are losing ground to bacteria that are now resistant to several drugs. The irony, of course, is that antibiotics developed to control bacteria have ...
PIAS-KT Educational Outreach
... – HAP/VAP is 2nd most common nosocomial infection in Canada – 5th most common non-surgical reason for IH admission ...
... – HAP/VAP is 2nd most common nosocomial infection in Canada – 5th most common non-surgical reason for IH admission ...
Impetigo: Diagnosis and Treatment
... Impetigo is the most common bacterial skin infection in children two to five years of age. There are two principal types: nonbullous (70% of cases) and bullous (30% of cases). Nonbullous impetigo, or impetigo contagiosa, is caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and is characteri ...
... Impetigo is the most common bacterial skin infection in children two to five years of age. There are two principal types: nonbullous (70% of cases) and bullous (30% of cases). Nonbullous impetigo, or impetigo contagiosa, is caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and is characteri ...
Management of Skin and Soft-Tissue Infection 132 Readersʼ Comments
... I would expect resolution with drainage alone, and quite promptly. This strikes me as a low risk situation for bacteremia, in comparison with many other serious S. aureus infections which are recognized late, or under treated, because patients and doctors do not understand the significance of pain w ...
... I would expect resolution with drainage alone, and quite promptly. This strikes me as a low risk situation for bacteremia, in comparison with many other serious S. aureus infections which are recognized late, or under treated, because patients and doctors do not understand the significance of pain w ...
PDF - International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
... important factor associated with the delayed wound healing is the bacterial biofilms that are polymicrobial and are mostly resistant to antibiotics. The present study was done to demonstrate the biofilm formation of the isolates from chronic and acute wound infection and its relation with multi-drug ...
... important factor associated with the delayed wound healing is the bacterial biofilms that are polymicrobial and are mostly resistant to antibiotics. The present study was done to demonstrate the biofilm formation of the isolates from chronic and acute wound infection and its relation with multi-drug ...
Effect of scrubs, gowns, masks on S aureus transmission ICHE Oct
... for all participants after rhinovirus exposure. Volunteers most often experienced nasal congestion, sore throat, and runny nose, followed by malaise, coughing, and headache. Sneezing and chills were reported least frequently. For 2 participants, nasal lavage specimens were not tested and serum titer ...
... for all participants after rhinovirus exposure. Volunteers most often experienced nasal congestion, sore throat, and runny nose, followed by malaise, coughing, and headache. Sneezing and chills were reported least frequently. For 2 participants, nasal lavage specimens were not tested and serum titer ...
PREVENTION AND CONTAINMENT OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS IN COMMUNITIES
... strains have evolved that affect previously healthy persons who have not had contact with health- ...
... strains have evolved that affect previously healthy persons who have not had contact with health- ...
If the does not start automatically click here
... regarding patient characteristics and vancomycin therapy were obtained from patients’ medical records. Statistical analyses were performed using descriptive statistics. Results: Out of 478 prescriptions for 365 patients, 79.1 % were considered inappropriate, based on HICPAC guidelines. This was main ...
... regarding patient characteristics and vancomycin therapy were obtained from patients’ medical records. Statistical analyses were performed using descriptive statistics. Results: Out of 478 prescriptions for 365 patients, 79.1 % were considered inappropriate, based on HICPAC guidelines. This was main ...
Antibiotic Susceptibility and mecAFrequency in Staphylococcus
... different genes such as antimicrobial resistance gene (2). Frequency of S. epidermidis isolates in this study was significantly lower than reports of Okee et al. (9), Eftekhar and Raei (10), Bouchami et al. (11), Barbier et al. (12), Ruppe et al. (13), and Mombach Pinheiro Machado AB et al. (14). In ...
... different genes such as antimicrobial resistance gene (2). Frequency of S. epidermidis isolates in this study was significantly lower than reports of Okee et al. (9), Eftekhar and Raei (10), Bouchami et al. (11), Barbier et al. (12), Ruppe et al. (13), and Mombach Pinheiro Machado AB et al. (14). In ...
Longevity Bulletin: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) (Issue 8)
... the overuse of antibiotics in many countries for medicinal and also agricultural purposes. Research into new antibiotics has not matched the evolution of the bacteria themselves; no new major class of proven antibiotics has been brought into clinical use since 1987 (although there are great hopes fo ...
... the overuse of antibiotics in many countries for medicinal and also agricultural purposes. Research into new antibiotics has not matched the evolution of the bacteria themselves; no new major class of proven antibiotics has been brought into clinical use since 1987 (although there are great hopes fo ...
The global burden of hygiene-related diseases in relation to the
... communities. A number of factors/events contribute to the current situation. • Despite significant investment at all levels, food-related, waterborne, and other non-food-related infectious intestinal diseases (IID) remain at unacceptably high levels, even in developed countries. This is despite the ...
... communities. A number of factors/events contribute to the current situation. • Despite significant investment at all levels, food-related, waterborne, and other non-food-related infectious intestinal diseases (IID) remain at unacceptably high levels, even in developed countries. This is despite the ...
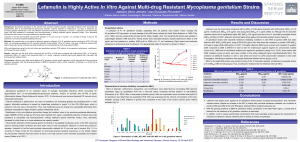
Lefamulin is Highly Active In Vitro Against Multi-drug
... approximately 25% of non-chlamydial-non-gonococcal urethritis. First-line treatment is azithromycin, but rates of resistance are increasing globally. Moxifloxacin is the only effective second-line therapy but resistance is common, in particular in the Asia-Pacific region and dual resistance to macro ...
... approximately 25% of non-chlamydial-non-gonococcal urethritis. First-line treatment is azithromycin, but rates of resistance are increasing globally. Moxifloxacin is the only effective second-line therapy but resistance is common, in particular in the Asia-Pacific region and dual resistance to macro ...
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (/ɛmɑrɛseɪ/ or /ˈmɜrsə/) is a bacterium responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It is also called oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (ORSA). MRSA is any strain of Staphylococcus aureus that has developed, through the process of natural selection, resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, which include the penicillins (methicillin, dicloxacillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, etc.) and the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, or MSSA. The evolution of such resistance does not cause the organism to be more intrinsically virulent than strains of S. aureus that have no antibiotic resistance, but resistance does make MRSA infection more difficult to treat with standard types of antibiotics and thus more dangerous.MRSA is especially troublesome in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where patients with open wounds, invasive devices, and weakened immune systems are at greater risk of nosocomial infection than the general public. MRSA began as a hospital-acquired infection, but has developed limited endemic status and is now sometimes community-acquired. The terms HA-MRSA (healthcare-associated MRSA) and CA-MRSA (community-associated MRSA) reflect this distinction.