* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biotechnology
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
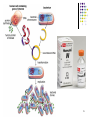
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
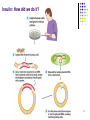
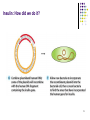
1 Biotechnology The use of gene science to create new products from plants and animals 2 Selective Breeding Also known as artificial selection Breed individuals with the desired trait together and the offspring should have the desired trait Often followed with inbreeding – breeding two of the offspring 3 4 5 6 Biotechnology Provides: Improved food products Longer shelf life, growing in more arid/colder environments, containing more vitamins Medical advances Creation and implementation of many medicines 7 Medical Advances: Diabetes and insulin With no effective treatment aside from a semistarvation diet, a diabetic's outlook appeared grim. Before 1922, diabetic children rarely lived a year after diagnosis, 5% of adults died within two years, and less than 20% lived more than ten. Untreated diabetics faced blindness, loss of limbs, kidney failure, stroke, heart attack and . 1869: It was discovered that those who died from diabetes all had a similar issue in their pancreas with the cells that created insulin 1920: insulin was extracted for the first time and used as an experiment on diabetic dogs 1922: The first human to received insulin. Leonard Thompson, a 14-year old boy dying of diabetes in Toronto. Thompson recovered and was discharged from the hospital 4 months later. With nothing to lose, many dying diabetics volunteered to be treated with insulin and had similar positive results 8 Medical Advances: Diabetes and insulin Death was averted but people with diabetes still suffered from allergic reactions and sores on the skin where they injected it. The insulin used was “impure” and generally a mixture from cows and pigs. Biosynthetic Insulin, introduced in 1983, was the first biotech product released and eliminated the need for animal pancreases. Synthesized insulin eliminates potential allergic reactions. Most insulins today are chemically identical to natural human insulin. 9 Recombinant DNA and Transgenic organisms Recombinant DNA – dna that is formed using parts from different organisms Transgenic organism – an organism that contains recombinant DNA Easiest organisms to use recombinant DNA on are bacteria because they take in loose DNA in a process call transformation. They also have “extra” DNA in their cells in the form of Plasmids. 10 11 Insulin: How did we do it? 12 Insulin: How did we do it? 13 Insulin: How did we do it? One cell with the recombinant plasmid *Growing bacteria is asexual reproduction – similar to mitosis but since they don’t have a nucleus (prokaryotes!) it is called binary fission A fermentor used to grow recombinant bacteria. 14 15 Biotechnology Breakthroughs Rice Enriched with beta-carotene and iron to benefit third world countries plagued by malnutrition Bananas Containing edible hepatitis vaccine making it capable to distribute in widespread easy manner Bacteria Used to break down oil after oil spills Viruses Used to target diseases and fight cancer 16 The great debate … Benefits Reduced pesticide/herbicide use Lower energy requirements Treat diseases Solves food production problems Greater crop yields Healthier products Downside: Future increase in greater use of pesticides/herbicides Create “super bugs” and “super weeds” Possible health ramifications Playing “God” Should they label products? Can you “own” a gene? 17