* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download doubling time
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
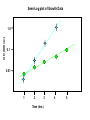
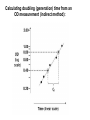
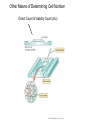
Bacteria are known for their rapid growth, many of the enterics will grow and then divide every 20 minutes under ideal conditions. Some bacteria isolated from deep underground may divide once every hundred years! Generation Time (doubling time): the amount of time required to double the number of cells in a culture. Measuring doubling time: theoretically: Nt = No x 2n by direct measurement: 1.) Turbidimetry: Semi-log plot of optical density (OD) vs. time 2.) Direct microscopic count 3.) Viability count Optical Density (OD) --- a measure of the number of objects in a light path (beam), generally also referred to as turbidimetry (requires a spectrophotometer) --- Absorbance (OD measure) is the decrease in the amount of light getting through the sample, usually the more sensitive measure --- Transmittance is the total amount of light penetrating the sample, doesn’t require as much optics as absorbance but is less sensitive --- OD (600nm): optical density taken with 600 nm light --- be aware that absorbance over 2.0 is not measured accurately by the spectrophotometer (sample will need to be diluted). --- above OD 0.4 scattered light is no longer proportional to cell density), very dense Cultures should be diluted by some known factor before another reading is taken (1/10 dilution is common) Semi-Log plot of Growth Data OD (600nm) 1.0 0.1 0.01 1 2 3 Time (hrs.) 4 5 Calculating doubling (generation) time from an OD measurement (indirect method): Other Means of Determining Cell Number Direct Count & Viability Count (cfu) Viability Count (Colony Forming Units, CFU) Serial Dilution Bacterial Growth Phases Microenvironments within a Test Tube What is the limiting factor to growth of a strict aerobe in this system other than O2? Factors for Bacterial Growth --- availability of nutrients (chapter 5) --- accumulation of metabolic byproducts (wastes) ---pH (protein structure, electron transport) --- oxygen (or lack there of) toxicity of oxygen --- temperature (protein structure) --- availability of water (food storage) Summary Chapter 6 Bacterial Growth --- know each phase of the growth curve and what the cells are experiencing in each phase --- aseptic technique -- culturing and media types How do you measure cell density? --- OD (growth curve) --- Direct Count --- Serial Dilution --- Water sampling Factors affecting bacterial growth --- be able to list several and explain them --- be able to define temperature classifications